Analysis of a "3-(Naphthalen-1-ylimino) Indoline-2-one" compound and Its Antimicrobial Assessment Using Lipid-based Self-nanoemulsifying Formulations
- PMID: 33375132
- PMCID: PMC7792971
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26010015
Analysis of a "3-(Naphthalen-1-ylimino) Indoline-2-one" compound and Its Antimicrobial Assessment Using Lipid-based Self-nanoemulsifying Formulations
Abstract
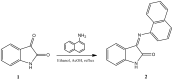
In recent years, indole derivatives have acquired conspicuous significance due to their wide spectrum of biological activities-antibacterial, antiviral, and anticonvulsant. This compound is derived from naturally grown plants. Therefore, synthesis of a novel "3-(Naphthalen-1-ylimino) indoline-2-one" compound (2) and its analysis using UPLC systems along with antimicrobial assessment was the aim of the current study. Isatin was used as a parent drug for synthesizing compound (2). Liquid Chromatographic analysis was performed using a C18 BEH column (1.7 µm 2.1 × 50 mm) by UPLC systems. Degradation studies were carried out to see whether acid, base, thermal, and oxidizing agents had any impact on the synthesized molecule in stress conditions (100 °C). A lipid-based self-nanoemulsifying formulation was developed and selectivity, specificity, recovery, accuracy, and precision were measured as part of the UPLC system's validation process. Antimicrobial studies were conducted using gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The standard samples were run with a concentration range of 5.0-100.0 µg/mL using the isocratic mobile phase comprising of methanol/water (70/30 %v/v) at 234 nm; good linearity (R2 = 0.9998) was found. The lower limits of detection (LOD) and quantitation (LOQ) of the method were found to be 0.81 µg/mL and 2.5 µg/mL, respectively. The coefficients of variation were found to be less than 2%. The antimicrobial study suggests that compound (2) has a substantial growth effect against gram-negative bacteria. It was successfully synthesized and applied to measure the concentrations in lipid-based dosage form, along with potent antimicrobial activities.
Keywords: 3-(Naphthalen-1-ylimino) indoline-2-one; UPLC systems; antimicrobial assessment; method validation; molecule synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest in the current study.
Figures






References
-
- Ratnamala P., Sonawane R.R.T. The chemistry and synthesis of 1H-indole-2,3-dione (Isatin) and its derivatives. Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astron. 2013;12:30–36.
-
- Singh U.K., Pandeya S.N., Singh A., Srivastava B.K., Pandey M. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Schiff’s and N-Mannich Bases of Isatin and Its Derivatives with 4-Amino-N-Carbamimidoyl Benzene Sulfonamide. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Drug Res. 2010;2:151–154.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

