Glenzocimab does not impact glycoprotein VI-dependent inflammatory haemostasis
- PMID: 33375772
- PMCID: PMC8252939
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2020.270439
Glenzocimab does not impact glycoprotein VI-dependent inflammatory haemostasis
Abstract
Not available.
Figures
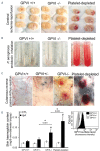
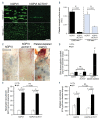
References
-
- Mangin PH, Tang CJ, Bourdon C, et al. . A humanized glycoprotein VI (GPVI) mouse model to assess the antithrombotic efficacies of anti-GPVI agents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012;341(1):156-163. - PubMed
-
- Dütting S, Bender M, Nieswandt B. Platelet GPVI: a target for antithrombotic therapy?! Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012;33(11):583-590. - PubMed
-
- Jiang P, Jandrot-Perrus M. New advances in treating thrombotic diseases: GPVI as a platelet drug target. Drug Discov Today. 2014; 19(9):1471-1475. - PubMed
-
- Stegner D, Haining EJ, Nieswandt B. Targeting glycoprotein vi and the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif signaling pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34(8):1615-1620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

