PLK1 Induces Chromosomal Instability and Overrides Cell-Cycle Checkpoints to Drive Tumorigenesis
- PMID: 33376114
- PMCID: PMC8026515
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-1377
PLK1 Induces Chromosomal Instability and Overrides Cell-Cycle Checkpoints to Drive Tumorigenesis
Abstract
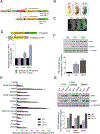
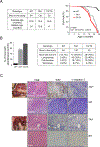
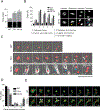
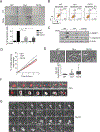
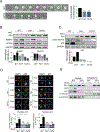
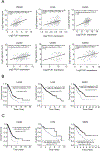
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is an essential cell-cycle regulator that is frequently overexpressed in various human cancers. To determine whether Plk1 overexpression drives tumorigenesis, we established transgenic mouse lines that ubiquitously express increased levels of Plk1. High Plk1 levels were a driving force for different types of spontaneous tumors. Increased Plk1 levels resulted in multiple defects in mitosis and cytokinesis, supernumerary centrosomes, and compromised cell-cycle checkpoints, allowing accumulation of chromosomal instability (CIN), which resulted in aneuploidy and tumor formation. Clinically, higher expression of PLK1 positively associated with an increase in genome-wide copy-number alterations in multiple human cancers. This study provides in vivo evidence that aberrant expression of PLK1 triggers CIN and tumorigenesis and highlights potential therapeutic opportunities for CIN-positive cancers. SIGNIFICANCE: These findings establish roles for PLK1 as a potent proto-oncogene and a CIN gene and provide insights for the development of effective treatment regimens across PLK1-overexpressing and CIN-positive cancers.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) and chromosomal instability in bladder cancer.Oncology. 2006;70(3):231-7. doi: 10.1159/000094416. Epub 2006 Jul 6. Oncology. 2006. PMID: 16837776
-
Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) overexpression enhances ionizing radiation-induced cancer formation in mice.J Biol Chem. 2017 Oct 20;292(42):17461-17472. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.810960. Epub 2017 Sep 12. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28900036 Free PMC article.
-
The Mitotic Cancer Target Polo-Like Kinase 1: Oncogene or Tumor Suppressor?Genes (Basel). 2019 Mar 11;10(3):208. doi: 10.3390/genes10030208. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30862113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plk1 overexpression induces chromosomal instability and suppresses tumor development.Nat Commun. 2018 Aug 1;9(1):3012. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05429-5. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30069007 Free PMC article.
-
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) signaling in cancer and beyond.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Nov;193:114747. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114747. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34454931 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Polo-Like Kinase 1 in Regulating the Forkhead Box Family Transcription Factors.Cells. 2023 May 8;12(9):1344. doi: 10.3390/cells12091344. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37174744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Combined Polo-Like-Kinase-1 Inhibitors and γ-Radiation Therapy.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 23;12(3):503. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030503. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540116 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal mechanisms of human centriole engagement and disengagement.EMBO J. 2025 Mar;44(5):1294-1321. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00350-8. Epub 2025 Feb 4. EMBO J. 2025. PMID: 39905228 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a novel PLK1 inhibitor with high inhibitory potency using a combined virtual screening strategy.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2025 Dec;40(1):2467798. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2025.2467798. Epub 2025 Mar 7. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40052927 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosuppression, immune escape, and immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer: focused on the tumor microenvironment.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023 Feb;46(1):17-48. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00741-1. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023. PMID: 36367669 Review.
References
-
- Zitouni S, Nabais C, Jana SC, Guerrero A, Bettencourt-Dias M. Polo-like kinases: structural variations lead to multiple functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Strebhardt K, Ullrich A. Targeting polo-like kinase 1 for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2006. - PubMed
-
- van Vugt MATM, van de Weerdt BCM, Vader G, Janssen H, Calafat J, Klompmaker R, et al. Polo-like kinase-1 is required for bipolar spindle formation but is dispensable for anaphase promoting complex/Cdc20 activation and initiation of cytokinesis. J Biol Chem, 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

