Paeoniflorin Alleviates Abnormalities in Rats with Functional Dyspepsia by Stimulating the Release of Acetylcholine
- PMID: 33376306
- PMCID: PMC7764555
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S260703
Paeoniflorin Alleviates Abnormalities in Rats with Functional Dyspepsia by Stimulating the Release of Acetylcholine
Abstract
Introduction: Paeoniflorin is a main active component in traditional Chinese medicine. Paeoniae alba radix is widely used as a spasmolytic and pain-relieving agent for abdominal spasmodic pain. Functional dyspepsia (FD) is characterized by pain or burning in the epigastrium, fullness, bloating and nausea. However, limited information is available about the effect of paeoniflorin on FD.
Materials and methods: In this study, iodoacetamide or clonidine-induced FD rat models were established to investigate the impacts of paeoniflorin on FD induced by different pathophysiologic disturbances.
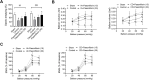
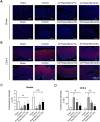
Results: We found the therapeutic effect of paeoniflorin through assessing the gastric emptying, gastric accommodation and visceral hypersensitivity. This function of paeoniflorin was related to the release of acetylcholine (ACh), which was accompanied by reduced acetylcholinesterase (AchE) activity in stomach and hypothalamus. Paeoniflorin administration inhibited the cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression and increased the level of ghrelin in the stomach. Besides, the levels of occludin and ZO-1 were elevated in the duodenum from paeoniflorin-treated rats, suggesting the impaired duodenal barrier was ameliorated.
Discussion: These results indicate that paeoniflorin possesses the ability to alleviate functional dyspepsia.
Keywords: acetylcholine; functional dyspepsia; gastric function; paeoniflorin.
© 2020 Zou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Enck P, Azpiroz F, Boeckxstaens G, et al. Functional dyspepsia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17081. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

