Irrational Responses to Risk Preference Questionnaires by Patients with Diabetes with or without Retinopathy and Comparison with Those without Diabetes
- PMID: 33376369
- PMCID: PMC7755883
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S283591
Irrational Responses to Risk Preference Questionnaires by Patients with Diabetes with or without Retinopathy and Comparison with Those without Diabetes
Abstract
Purpose: The risk preferences of patients with diabetes have profound effects on the progression of complications. The present study aimed to clarify whether the preferences of patients with diabetes and retinopathy are deliberately risk-seeking or irrational and whether this propensity is specific to those with retinopathy or is also found in patients without retinopathy compared with those without diabetes.
Patients and methods: A total of 394 patients with diabetes (264 without retinopathy and 130 with retinopathy) and 198 patients without diabetes agreed to participate in this survey. The questions were modified versions of those from the Japan Household Survey on Consumer Preferences and Satisfaction, which sought to determine the participants' personal socioeconomic status and risk preferences. In the questionnaires, responses were analyzed by determining the participants' willingness to pay for a lottery ticket and for an insurance policy. Irrational responses were defined as violations of two axioms of the Expected Utility Theory: completeness and transitivity.
Results: The incidence of irrational responses increased with age and was associated with educational level. The incidence of irrational responses was significantly higher in patients with retinopathy than in those without retinopathy after adjusting for age and educational level. There was no significant difference in the incidence of irrational responses between patients with diabetes but without retinopathy and those without diabetes.
Conclusion: The risk-seeking behavior of patients with diabetes and retinopathy was not deliberate but was irrational under uncertainty. Medical professionals should be aware of their patients' propensity to make irrational decisions, which is an important risk factor for the progression of retinopathy in patients with diabetes regardless of age and educational level.
Keywords: behavioral economics; cognitive function; educational level; expected utility theory.
© 2020 Emoto et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

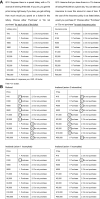
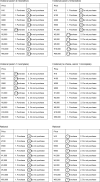
Similar articles
-
A socioeconomic and behavioral survey of patients with difficult-to-control type 2 diabetes mellitus reveals an association between diabetic retinopathy and educational attainment.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2016 Oct 25;10:2151-2162. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S116198. eCollection 2016. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2016. PMID: 27822016 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral economics survey of patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2015 May 11;9:649-58. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S82022. eCollection 2015. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2015. PMID: 25999700 Free PMC article.
-
Is expected utility theory normative for medical decision making?Med Decis Making. 1996 Jan-Mar;16(1):1-6. doi: 10.1177/0272989X9601600101. Med Decis Making. 1996. PMID: 8717589
-
[Irrational drug use in Siauliai, Panevezys and Utena counties of Lithuania].Medicina (Kaunas). 2003;39 Suppl 2:9-18. Medicina (Kaunas). 2003. PMID: 14617852 Review. Lithuanian.
-
Optimizing Medical Management for Patients with Diabetes-Related Retinopathy.In: Prevention and Management of Diabetes-Related Eye Disease. Arlington (VA): American Diabetes Association; 2019 May. In: Prevention and Management of Diabetes-Related Eye Disease. Arlington (VA): American Diabetes Association; 2019 May. PMID: 34251787 Free Books & Documents. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Risk Preferences, Rationality of Choices, and Willingness to Pay for Preventive Medicine in Patients with Graves' Thyrotoxicosis.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2021 Sep 7;15:1971-1979. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S323472. eCollection 2021. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2021. PMID: 34522090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chatterjee S, Khunti K, Davies MJ. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2017;389(10085):2239–2251. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

