Nomogram Based on Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Coronary Heart Disease
- PMID: 33376372
- PMCID: PMC7756175
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S273880
Nomogram Based on Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Coronary Heart Disease
Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to study risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients and establish a clinical prediction model.
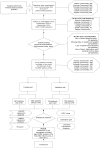
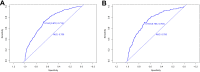
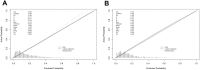
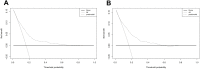
Research design and methods: A total of 3402 T2DM patients were diagnosed by clinical doctors and recorded in the electronic medical record system (EMRS) of six Community Health Center Hospitals from 2015 to 2017, including the communities of Huamu, Jinyang, Yinhang, Siping, Sanlin and Daqiao. From September 2018 to September 2019, 3361 patients (41 patients were missing) were investigated using a questionnaire, physical examination, and biochemical index test. After excluding the uncompleted data, 3214 participants were included in the study and randomly divided into a training set (n = 2252) and a validation set (n = 962) at a ratio of 3:1. Through lead absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression analysis and logistic regression analysis of the training set, risk factors were determined and included in a nomogram. The C-index, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, calibration plot and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to validate the distinction, calibration and clinical practicality of the model.
Results: Age, T2DM duration, hypertension (HTN), hyperuricaemia (HUA), body mass index (BMI), glycosylated haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), high-density lipoprotein (HDL-C) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C) were significant factors in this study. The C-index was 0.750 (0.724-0.776) based on the training set and 0.767 (0.726-0.808) based on the validation set. Through ROC analysis, the set area was 0.750 for the training set and 0.755 for the validation set. The calibration test indicated that the S:P of the prediction model was 0.982 in the training set and 0.499 in the validation set. The decision curve analysis showed that the threshold probability of the model was 16-69% in the training set and 16-73% in the validation set.
Conclusion: Based on community surveys and data analysis, a prediction model of CHD in T2DM patients was established.
Keywords: coronary heart disease; prediction model; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2020 Shi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development and External Validation of Nomogram to Identify Risk Factors for CHD in T2DM in the Population of Northwestern China.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 May 4;16:1271-1282. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S404683. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 37168834 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Risk Factors for Hyperuricaemia and Related Vascular Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2020 Sep 21;13:1661-1675. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S255042. eCollection 2020. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2020. PMID: 33061700 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive nomogram for coronary heart disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Nov 10;9:1052547. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1052547. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36440044 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of Clinical Prediction Model Based on the Study of Risk Factors of Stroke in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Aug 25;11:559. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00559. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32982965 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a Risk Prediction Model for Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Type 2 Diabetes.Diabetes Ther. 2020 Sep;11(9):2057-2073. doi: 10.1007/s13300-020-00893-z. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Diabetes Ther. 2020. PMID: 32725485 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of a nomogram to predict mortality risk in patients with ischemic heart disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Feb 16;10:1115463. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1115463. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36873413 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Atrial Fibrillation in Hospitalized Elderly Patients With Coronary Heart Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Machine Learning: A Multicenter Retrospective Study.Front Public Health. 2022 Mar 4;10:842104. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.842104. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35309227 Free PMC article.
-
Nomogram based on multimodal echocardiography for assessing the evolution of diabetic cardiomyopathy in diabetic patients with normal cardiac function.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Sep 20;9:1002509. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1002509. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36204578 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal expression of long non-coding RNA rhabdomyosarcoma 2-associated transcript (RMST) participates in the pathological mechanism of atherosclerosis by regulating miR-224-3p.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):2648-2657. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2023995. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35067166 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis risk factors of long-term adverse outcomes and a prediction nomogram for coronary artery disease patients underwent fractional flow reserve.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Feb 18;22(6):1292-1300. doi: 10.7150/ijms.106807. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40084257 Free PMC article.
References
-
- IDF. Available from: https://diabetesatlas.org/en/. Accessed December 10, 2020.
-
- International Diabetes Federation IDF Diabetes Atlas. Epidemiology and morbidity. Available from: https://diabetesatlas.org/en/.Accessed December 10, 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

