The Significance of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Combined Chemoradiotherapy in Patients Undergoing Bladder Preservation Therapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 33376404
- PMCID: PMC7764706
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S283954
The Significance of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Combined Chemoradiotherapy in Patients Undergoing Bladder Preservation Therapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
Abstract
Background: Bladder-sparing treatment has been developed with the aim of preserving bladder function. However, considerable controversy remains regarding the effectiveness of organ preservation strategies. Accordingly, we investigated factors influencing the prognosis of muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) patients who received bladder-sparing treatment.
Materials and methods: In the study, we retrospectively reviewed 193 patients who were newly diagnosed with MIBC and received bladder-sparing treatment from 2006 to 2013 in our hospital.
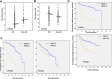
Results: The 5-year overall survival, progression-free survival (PFS) and bladder-preservation survival rates after diagnosis were 64.7%, 52.1%, and 64%, respectively. The presence of hydronephrosis, advanced stage and not achieving complete response were associated with a marked reduction in PFS. Treatment with an adequate dose of combined chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) (chemotherapy ≥2 cycles combined with radiotherapy dose ≥56Gy) significantly improved the complete response (CR), 5-year bladder-preservation survival, and PFS rates, particularly for patients with good performance status. The 5-year bladder-preservation survival rates for CR and non-CR patients were 75%, and 21%, respectively. Furthermore, higher pre-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) (≥3) and lower hemoglobin (≤12) were significantly associated with lower CR rate, increased risk of loco-regional recurrence and reduced bladder-preservation survival rate. Multivariable Cox regression analysis based on different co-variables showed that pretreatment NLR was an independent prognostic factor for PFS when MIBC patients were stratified by clinical stage and the doses of CCRT.
Conclusion: In MIBC patients with bladder-sparing treatment, adequate doses of CCRT and low NLR were found to be correlated with better PFS. We suggest the use of NLR as a clinical biomarker for the prognosis of MIBC and guidance of treatment decisions.
Keywords: MIBC; NLR; bladder-sparing; radiotherapy; recurrence.
© 2020 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

