The Use of Single Dose Methotrexate in the Management of Ectopic Pregnancy and Pregnancy of Unknown Location: 10 Years' Experience in a Tertiary Center
- PMID: 33376413
- PMCID: PMC7764964
- DOI: 10.2147/IJWH.S279426
The Use of Single Dose Methotrexate in the Management of Ectopic Pregnancy and Pregnancy of Unknown Location: 10 Years' Experience in a Tertiary Center
Abstract
Objective: To study factors associated with the success of single dose methotrexate (MTX) treatment in women with ectopic pregnancy.
Methods: This is a retrospective study of women (n=110) with ectopic pregnancy and treated with single dose of MTX. The clinical presentations, transvaginal sonography (TVS) findings, pretreatment beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-HCG), and progesterone values were compared between the treatment success (Group S) and treatment failure (Group F) groups.
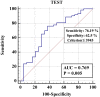
Results: The overall success rate of treatment with single dose of MTX was 75.45%. The majority of patients in both groups presented with pain and bleeding (~55%), and bleeding only was the presenting symptom in about 20% of patients. Only 3 patients (3.61%) in Group S required a repeat dose of MTX. In contrast, 51.8% of the Group F patients required a repeat dose. The mean pretreatment β-HCG level was 2.3 times higher in Group F than in Group S (1734±1684 vs 4036±2940 IU/L). The data showed a β-HCG level of 3924IU/L as a suitable cut-off value with 76.19% sensitivity and 62.5% specificity to predict MTX treatment success. History of ectopic pregnancy had no relation with success/treatment failure or a repeat dose. None of the TVS findings were related to the outcome of the treatment, whereas pretreatment HCG level was a significant predictor.
Conclusion: The single dose MTX treatment was successful in 75.45% (83/110) of cases, with 3.61% (3/83) requiring a repeat dose of the drug. Pretreatment β-HCG level is a significant predictor of the treatment outcome.
Keywords: ectopic pregnancy; methotrexate; pretreatment β HCG.
© 2020 Sindiani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cutoff value of human chorionic gonadotropin in relation to the number of methotrexate cycles in the successful treatment of ectopic pregnancy.Fertil Steril. 2009 Oct;92(4):1203-1207. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.07.1775. Epub 2008 Oct 11. Fertil Steril. 2009. PMID: 18851850
-
Methotrexate or expectant management in women with an ectopic pregnancy or pregnancy of unknown location and low serum hCG concentrations? A randomized comparison.Hum Reprod. 2013 Jan;28(1):60-7. doi: 10.1093/humrep/des373. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Hum Reprod. 2013. PMID: 23081873 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy with methotrexate.Acta Clin Croat. 2012 Dec;51(4):543-8. Acta Clin Croat. 2012. PMID: 23540161
-
Methotrexate vs placebo in early tubal ectopic pregnancy: a multi- centre double-blind randomised trial.Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2012 Aug;7(3):238-43. doi: 10.2174/157488712802281321. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2012. PMID: 22540910 Review.
-
Overview and guidelines of off-label use of methotrexate in ectopic pregnancy: report by CNGOF.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2016 Oct;205:105-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2016.07.489. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2016. PMID: 27572300 Review.
Cited by
-
Future Perspectives of Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment-Review of Possible Pharmacological Methods.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 31;19(21):14230. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192114230. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36361110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the risk factors and management outcomes of ectopic pregnancy: A retrospective case-control study.Int J Reprod Biomed. 2023 May 12;21(5):403-414. doi: 10.18502/ijrm.v21i5.13475. eCollection 2023 May. Int J Reprod Biomed. 2023. PMID: 37362094 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of Successful Medical Management With Methotrexate in Unruptured Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy.Cureus. 2022 Nov 26;14(11):e31923. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31923. eCollection 2022 Nov. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36580082 Free PMC article.
-
Ruptured ovarian ectopic pregnancy in a primigravid woman: A case report.Int J Reprod Biomed. 2024 Mar 25;22(2):157-160. doi: 10.18502/ijrm.v22i2.15713. eCollection 2024 Feb. Int J Reprod Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38628777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnhart KT, Gosman G, Ashby R, Sammel M. The medical management of ectopic pregnancy: a meta-analysis comparing “single dose” and “multidose” regimens. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;101:778–784. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources