Galactorrhoea and Hyperprolactinaemia in a Non-Pregnant Female with Burns
- PMID: 33376475
- PMCID: PMC7745297
Galactorrhoea and Hyperprolactinaemia in a Non-Pregnant Female with Burns
Abstract
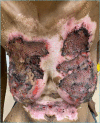
Galactorrhoea is the presence of breast milk secretion in non-pregnant or non-breastfeeding females. In females with galactorrhoea and amenorrhoea, hyperprolactinaemia is the most likely cause. Chest wall pathology is a known cause of hyperprolactinaemia, however there are few documented reports on galactorrhoea following burn injury to the chest wall. We report a case of an adult female patient who sustained hot water burns to her torso. Following the second skin graft failure, galactorrhoea was noted and investigated. Hyperprolactinaemia was found with normal renal and thyroid function. There were no abnormalities detected on the hormones in the hypothalamic pituitary axis and MRI. Hyperprolactinaemia was attributed to chest wall injuries causing pathological stimulation of the neural suckling reflex. The patient was treated with dopamine agonists for one month and the galactorrhoea disappeared. Treatment was discontinued on discharge and the prolactin levels remained normal upon follow-up visit to the clinic.
Keywords: chest burns; galactorrhoea; hyperprolactinaemia; prolactin.
Copyright © 2020 International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (IFCC). All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Leung AKC, Pacaud D. Diagnosis and management of galactorrhea. Am Fam Physician. 2004;70(3):543-550. - PubMed
-
- Bernard V, Young J, Chanson P, Binart N. New insights in prolactin: pathological implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015; 11:265–275. - PubMed
-
- Kavanagh L, McKenna TJ, Fahie-Wilson MN, Gibney J, Smith TP. Specificity and Clinical Utility of Methods for the Detection of Macroprolactin. Clin Chem. 2006;52(7): 1366–1372. - PubMed
-
- Melmed S, Casanueva FF, Hoffman AR, Kleinberg DL, Montori VM, Schlechte JA, et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyperprolactinemia: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(2): 273–288. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources