Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by regulating the balance of Th17/Treg cells and inhibiting the NF- κ B signaling pathway
- PMID: 33376516
- PMCID: PMC7751469
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9566
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by regulating the balance of Th17/Treg cells and inhibiting the NF- κ B signaling pathway
Abstract
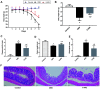
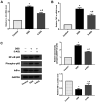
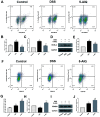
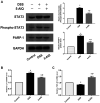
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) plays a critical role in inflammatory pathways. The PARP-1 inhibitor, 5-aminoisoquinolinone (5-AIQ), has been demonstrated to exert significant pharmacological effects. The present study aimed to further examine the potential mechanisms of 5-AIQ in a mouse model of dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis. Colitis conditions were assessed by changes in weight, disease activity index, colon length, histopathology and pro-inflammatory mediators. The colonic expression of PARP/NF-κB and STAT3 pathway components was measured by western blot analysis. Flow cytometry was used to analyze the proportion of T helper 17 cells (Th17) and regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the spleen. Western blot analysis and reverse transcription-quantitative PCR were employed to determine the expression of the transcription factors retinoic acid-related orphan receptor and forkhead box protein P3. The results demonstrated that 5-AIQ reduced tissue damage and the inflammatory response in mice with experimental colitis. Moreover, 5-AIQ increased the proportion of Treg cells and decreased the percentage of Th17 cells in the spleen. Furthermore, following 5-AIQ treatment, the main components of the PARP/NF-κB and STAT3 pathways were downregulated. Collectively, these results demonstrate that the PARP-1 inhibitor, 5-AIQ, may suppress intestinal inflammation and protect the colonic mucosa by modulating Treg/Th17 immune balance and inhibiting PARP-1/NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways in mice with experimental colitis.
Keywords: 5-aminoisoquinolinone; T helper 17 cell; poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor; regulatory T cell; ulcerative colitis.
Copyright: © Peng et al.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
