LINC00488 stimulates the progression of esophageal cancer by targeting microRNA-485-5p
- PMID: 33376519
- PMCID: PMC7751374
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.12347
LINC00488 stimulates the progression of esophageal cancer by targeting microRNA-485-5p
Retraction in
-
LINC00488 stimulates the progression of esophageal cancer by targeting microRNA-485-5p.Oncol Lett. 2022 Jul 4;24(3):292. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13412. eCollection 2022 Sep. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35949595 Free PMC article.
Abstract
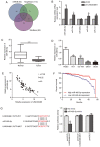
Esophageal cancer is the eighth most prevalent malignancy in the world and China has a high incidence of esophageal cancer. Previous studies have identified that LINC00488 is an oncogene; however, its role in esophageal cancer remains unclear. The present study detected the expression and biological functions of LINC00488 in the progression of esophageal cancer. LINC00488 levels in 45 esophageal cancer and matched paracancerous tissues were detected. The association between LINC00488 level, clinical indexes and overall survival rate of patients with esophageal cancer was analyzed. Using Cell Counting Kit-8, Transwell and wound healing assays, the influence of LINC00488 on the biological functions of OE19 and OE33 cells were assessed. The target gene of LINC00488, microRNA-485-5p (miRNA-485-5p), was predicted using bioinformatics databases. In addition, the role of miRNA-485-5p in the progression of esophageal cancer was evaluated using rescue experiments. LINC00488 was upregulated in esophageal cancer tissues and cell lines. A high level of LINC00488 was associated with lymphatic and distant metastasis and poor prognosis in patients with esophageal cancer. Silencing LINC00488 attenuated the viability, migration and wound healing of OE19 and OE33 cells. miRNA-485-5p was downregulated in esophageal cancer and low expression levels predicted a poor prognosis in these patients. In addition, miRNA-485-5p level was negatively correlated with that of LINC00488. Rescue experiments showed that knockdown of miRNA-485-5p reversed the attenuated proliferation and migration of esophageal cancer cells with LINC00488-knockdown. In conclusion, LINC00488 aggravated the malignant progression of esophageal cancer by targeting miRNA-485-5p.
Keywords: LINC00488; esophageal cancer; malignant progression; microRNA-485-5p.
Copyright: © Xu et al.
Figures



References
-
- Lu HB. MicroRNA-556-3p promotes the progression of esophageal cancer via targeting DAB2IP. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22:6816–6823. - PubMed
-
- Cheng Z, Geng H, Cheng Y, Dong N, Ning F, Yu Z, Jian J, Chen S. Effects of MiR-210 on proliferation, apoptosis and invasion abilities of esophageal cancer cells. J BUON. 2018;23:814–819. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
