Synergism and Antagonism of Two Distinct, but Confused, Nrf1 Factors in Integral Regulation of the Nuclear-to-Mitochondrial Respiratory and Antioxidant Transcription Networks
- PMID: 33376579
- PMCID: PMC7744186
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/5097109
Synergism and Antagonism of Two Distinct, but Confused, Nrf1 Factors in Integral Regulation of the Nuclear-to-Mitochondrial Respiratory and Antioxidant Transcription Networks
Abstract
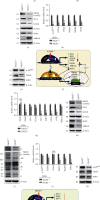
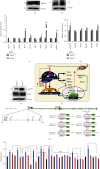
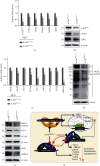
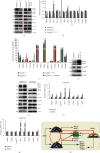
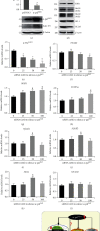
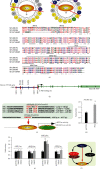
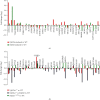
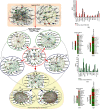
There is hitherto no literature available for explaining two distinct, but confused, Nrf1 transcription factors, because they shared the same abbreviations from nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 1 (also called Nfe2l1) and nuclear respiratory factor (originally designated α-Pal). Thus, we have here identified that Nfe2l1Nrf1 and α-PalNRF1 exert synergistic and antagonistic roles in integrative regulation of the nuclear-to-mitochondrial respiratory and antioxidant transcription profiles. In mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), knockout of Nfe2l1-/- leads to substantial decreases in expression levels of α-PalNRF1 and Nfe2l2, together with TFAM (mitochondrial transcription factor A) and other target genes. Similar inhibitory results were determined in Nfe2l2-/- MEFs but with an exception that both GSTa1 and Aldh1a1 were distinguishably upregulated in Nfe2l1-/- MEFs. Such synergistic contributions of Nfe2l1 and Nfe2l2 to the positive regulation of α-PalNRF1 and TFAM were validated in Keap1-/- MEFs. However, human α-PalNRF1 expression was unaltered by hNfe2l1α-/- , hNfe2l2-/-ΔTA , or even hNfe2l1α-/-+siNrf2, albeit TFAM was activated by Nfe2l1 but inhibited by Nfe2l2; such an antagonism occurred in HepG2 cells. Conversely, almost all of mouse Nfe2l1, Nfe2l2, and cotarget genes were downexpressed in α-PalNRF1+/- MEFs. On the contrary, upregulation of human Nfe2l1, Nfe2l2, and relevant reporter genes took place after silencing of α-PalNRF1, but their downregulation occurred upon ectopic expression of α-PalNRF1. Furtherly, Pitx2 (pituitary homeobox 2) was also identified as a direct upstream regulator of Nfe2l1 and TFAM, besides α-PalNRF1. Overall, these across-talks amongst Nfe2l1, Nfe2l2, and α-PalNRF1, along with Pitx2, are integrated from the endoplasmic reticulum towards the nuclear-to-mitochondrial communication for targeting TFAM, in order to finely tune the robust balance of distinct cellular oxidative respiratory and antioxidant gene transcription networks, albeit they differ between the mouse and the human. In addition, it is of crucial importance to note that, in view of such mutual interregulation of these transcription factors, much cautions should be severely taken for us to interpret those relevant experimental results obtained from knockout of Nfe2l1, Nfe2l2, α-Pal or Pitx2, or their gain-of-functional mutants.
Copyright © 2020 Shuwei Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

