Higher Serum-Soluble α-Klotho Level Does Not Predict Longer Survival after Stroke
- PMID: 33376748
- PMCID: PMC7738777
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/9283651
Higher Serum-Soluble α-Klotho Level Does Not Predict Longer Survival after Stroke
Abstract
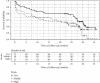
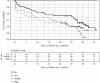
Results: There were 5 recurrent strokes and 89 deaths during the 36-month follow-up. Even though no significant differences in OS and SFS between soluble α-Klotho level tertile groups were recorded, unexpectedly, OS and SFS were highest in patients with the lowest soluble α-Klotho concentrations. Moreover, the Cox proportional models adjusted for established risk factors, kidney function, and the severity of stroke revealed that each 100 pg/mL increase in soluble α-Klotho levels was associated with decreased OS (HR = 0.951 (0.908-0.995), p < 0.05) and SFS (HR = 0.949 (0.908-0.993), p < 0.05). In addition, the α-Klotho to iFGF23 index was predicting neither OS nor SFS.
Conclusion: Soluble α-Klotho levels in serum were not related to the severity of neurological deficits and long-term outcomes in patients with IS. No neuroprotective effect of soluble α-Klotho levels in patients with IS was demonstrated.
Copyright © 2020 Dagmara Adamska-Tomaszewska et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Liu X. Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms and combination genotype distributions of the KL gene with essential hypertension in the aged. Journal of Chongqing Medical University. 2011;4, article R544.1
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical