Carbon Dots: A New Type of Carbon-Based Nanomaterial with Wide Applications
- PMID: 33376780
- PMCID: PMC7760469
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.0c01306
Carbon Dots: A New Type of Carbon-Based Nanomaterial with Wide Applications
Abstract
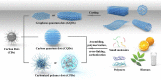
Carbon dots (CDs), as a new type of carbon-based nanomaterial, have attracted broad research interest for years, because of their diverse physicochemical properties and favorable attributes like good biocompatibility, unique optical properties, low cost, ecofriendliness, abundant functional groups (e.g., amino, hydroxyl, carboxyl), high stability, and electron mobility. In this Outlook, we comprehensively summarize the classification of CDs based on the analysis of their formation mechanism, micro-/nanostructure and property features, and describe their synthetic methods and optical properties including strong absorption, photoluminescence, and phosphorescence. Furthermore, the recent significant advances in diverse applications, including optical (sensor, anticounterfeiting), energy (light-emitting diodes, catalysis, photovoltaics, supercapacitors), and promising biomedicine, are systematically highlighted. Finally, we envisage the key issues to be challenged, future research directions, and perspectives to show a full picture of CDs-based materials.
© 2020 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





References
-
- Liu M. L.; Chen B. B.; Li C. M.; Huang C. Z. Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Formation Mechanism, Fluorescence Origin and Sensing Applications. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 449–471. 10.1039/C8GC02736F. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

