Transcranial magnetic stimulation reveals diminished homoeostatic metaplasticity in cognitively impaired adults
- PMID: 33376989
- PMCID: PMC7750948
- DOI: 10.1093/braincomms/fcaa203
Transcranial magnetic stimulation reveals diminished homoeostatic metaplasticity in cognitively impaired adults
Abstract
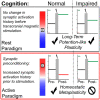
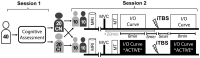
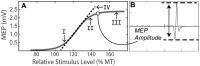
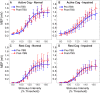
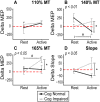
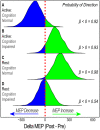
Homoeostatic metaplasticity is a neuroprotective physiological feature that counterbalances Hebbian forms of plasticity to prevent network destabilization and hyperexcitability. Recent animal models highlight dysfunctional homoeostatic metaplasticity in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. However, the association between homoeostatic metaplasticity and cognitive status has not been systematically characterized in either demented or non-demented human populations, and the potential value of homoeostatic metaplasticity as an early biomarker of cognitive impairment has not been explored in humans. Here, we report that, through pre-conditioning the synaptic activity prior to non-invasive brain stimulation, the association between homoeostatic metaplasticity and cognitive status could be established in a population of non-demented human subjects (older adults across cognitive spectrums; all within the non-demented range). All participants (n = 40; age range, 65-74, 47.5% female) underwent a standardized neuropsychological battery, magnetic resonance imaging and a transcranial magnetic stimulation protocol. Specifically, we sampled motor-evoked potentials with an input/output curve immediately before and after repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation to assess neural plasticity with two experimental paradigms: one with voluntary muscle contraction (i.e. modulated synaptic activity history) to deliberately introduce homoeostatic interference, and one without to serve as a control condition. From comparing neuroplastic responses across these experimental paradigms and across cohorts grouped by cognitive status, we found that (i) homoeostatic metaplasticity is diminished in our cohort of cognitively impaired older adults and (ii) this neuroprotective feature remains intact in cognitively normal participants. This novel finding suggests that (i) future studies should expand their scope beyond just Hebbian forms of plasticity that are traditionally assessed when using non-invasive brain stimulation to investigate cognitive ageing and (ii) the potential value of homoeostatic metaplasticity in serving as a biomarker for cognitive impairment should be further explored.
Keywords: TMS; cognitive ageing; dementia; mild cognitive impairment; plasticity.
© The Author(s) (2020). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott LF, Nelson SB. Synaptic plasticity: taming the beast. Nat Neurosci 2000; 3: 1178–83. - PubMed
-
- Abraham WC. Metaplasticity: tuning synapses and networks for plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 2008; 9: 387–99. - PubMed
-
- Abraham WC, Bear MF. Metaplasticity : plasticity of synaptic. Trends Neurosci 1996; 19: 126–30. - PubMed
-
- Abraham WC, Robins A. Memory retention—the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma. Trends Neurosci 2005; 28: 73–8. - PubMed
-
- Amatniek JC, Hauser WA, DelCastillo-Castaneda C, Jacobs DM, Marder K, Bell K, et al. Incidence and predictors of seizures in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Epilepsia 2006; 47: 867–72. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
