Protocol for Site-Specific Photo-Crosslinking Proteomics to Identify Protein-Protein Interactions in Mammalian Cells
- PMID: 33377005
- PMCID: PMC7756934
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2020.100109
Protocol for Site-Specific Photo-Crosslinking Proteomics to Identify Protein-Protein Interactions in Mammalian Cells
Abstract
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) play essential roles in almost all aspects of cellular processes. However, PPIs remain challenging to study due to their substoichiometry, low affinity, dynamic nature, and context dependence. Here, we present a protocol for the capture and identification of PPIs in live mammalian cells, which relies on site-specific photo-crosslinking in live cells, affinity purification, and quantitative proteomics. The protocol facilitates efficient and reliable identification of the interacting proteins of a given protein of interest in live cells. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Wu et al. (2020).
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
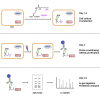
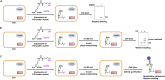
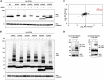
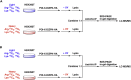
References
-
- Chin J.W. Expanding and reprogramming the genetic code. Nature. 2017;550:53–60. - PubMed
-
- Cox J., Mann M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008;26:1367–1372. - PubMed
-
- He D., Xie X., Yang F., Zhang H., Su H., Ge Y., Song H., Chen P.R. Quantitative and comparative profiling of protease substrates through a genetically encoded multifunctional photocrosslinker. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017;56:14521–14525. - PubMed
-
- Lin S., He D., Long T., Zhang S., Meng R., Chen P.R. Genetically encoded cleavable protein photo-cross-linker. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014;136:11860–11863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

