Preparing Highly Viable Single-Cell Suspensions from Mouse Pancreatic Islets for Single-Cell RNA Sequencing
- PMID: 33377038
- PMCID: PMC7757316
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2020.100144
Preparing Highly Viable Single-Cell Suspensions from Mouse Pancreatic Islets for Single-Cell RNA Sequencing
Abstract
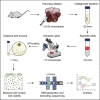
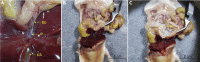
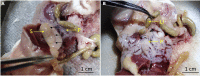
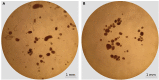
Pancreatic islets consist of several cell types, including alpha, beta, delta, epsilon, and PP cells. Due to cellular heterogeneity, it is challenging to interpret whole-islet transcriptome data. Single-cell transcriptomics offers a powerful method for investigating gene expression at the single-cell level and identifying cellular heterogeneity and subpopulations. Here, we describe a protocol for mouse pancreatic islet isolation, culturing, and dissociation into a single-cell suspension. This protocol yields highly viable cells for successful library preparation and single-cell RNA sequencing. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Lee et al. (2020).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- McCall M.D., Maciver A.H., Pawlick R., Edgar R., Shapiro A.M. Histopaque provides optimal mouse islet purification kinetics: comparison study with Ficoll, iodixanol and dextran. Islets. 2011;3:144–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

