ACCELERATE: A Patient-Powered Natural History Study Design Enabling Clinical and Therapeutic Discoveries in a Rare Disorder
- PMID: 33377129
- PMCID: PMC7762771
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100158
ACCELERATE: A Patient-Powered Natural History Study Design Enabling Clinical and Therapeutic Discoveries in a Rare Disorder
Abstract
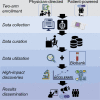
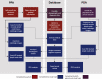
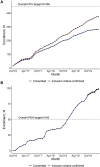
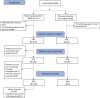
Geographically dispersed patients, inconsistent treatment tracking, and limited infrastructure slow research for many orphan diseases. We assess the feasibility of a patient-powered study design to overcome these challenges for Castleman disease, a rare hematologic disorder. Here, we report initial results from the ACCELERATE natural history registry. ACCELERATE includes a traditional physician-reported arm and a patient-powered arm, which enables patients to directly contribute medical data and biospecimens. This study design enables successful enrollment, with the 5-year minimum enrollment goal being met in 2 years. A median of 683 clinical, laboratory, and imaging data elements are captured per patient in the patient-powered arm compared with 37 in the physician-reported arm. These data reveal subgrouping characteristics, identify off-label treatments, support treatment guidelines, and are used in 17 clinical and translational studies. This feasibility study demonstrates that the direct-to-patient design is effective for collecting natural history data and biospecimens, tracking therapies, and providing critical research infrastructure.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02817997.
Keywords: Castleman disease; direct-to-patient; natural history registry; orphan disease; patient-powered.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
A.L. reports employment and equity ownership from BridgeBio Pharma. A.R. reports consultancy to LabCorp and Consonance Capital, board member of Safeguard Biosystems, and member of academic advisory council to AMN. S.F. reports consultancy, advisory board membership, research funding, and speakers’ honoraria from Janssen Pharmaceuticals; consultancy, advisory board membership, and speakers’ honoraria from EUSA Pharma; advisory board membership in Clinigen; speakers’ honoraria from Servier; and research funding from Gilead. P.L.Z. reports consultancy to Verastem, MSD, EUSA Pharma, and Sanofi; speakers’ bureau of Verastem, Celltrion, Gilead, Janssen-Cilag, BMS, Servier, MSD, Immune Design, Celgene, Portola, Roche, EUSA Pharma, and Kyowa Kirin; advisory board membership in Verastem, Celltrion, Gilead, and Janssen-Cilag, BMS, Servier, Sandoz, MSD, Immune Design, Celgene, Portola, Roche, EUSA Pharma, Kyowa Kirin, and Sanofi. L.T. reports advisory board membership in EUSA Pharma. C.C. reports consultancy to EUSA Pharma. E.O. reports advisory board membership in and consultancy to EUSA Pharma. G.S. reports speakers’ bureau involvement with Takeda, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Foundation Medicine, and EUSA Pharma. T.S.U. reports research support from Roche and Celgene and receives study drug for a clinical trial from Merck. F.v.R. reports a consultancy relationship with Takeda, Sanofi Genzyme, EUSA Pharma, Adicet Bio, Kite Pharma, and Karyopharm Therapeutics. D.C.F. reports research funding from Janssen Pharmaceuticals (former financial sponsor) and EUSA Pharma (current financial sponsor) for the ACCELERATE Natural History Registry, donation of study drug from Pfizer for NCT03933904, and a provisional patent application filed by the University of Pennsylvania for Methods of Treating Idiopathic Multicentric Castleman disease with JAK1/2 inhibition (62/989,437). All of the other authors report no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Global Genes. Rare facts. https://globalgenes.org/rare-facts/.
-
- Kempf L., Goldsmith J.C., Temple R. Challenges of developing and conducting clinical trials in rare disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2018;176:773–783. - PubMed
-
- Fajgenbaum D.C., Shilling D. Castleman Disease Pathogenesis. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2018;32:11–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

