Epothilones Improve Axonal Growth and Motor Outcomes after Stroke in the Adult Mammalian CNS
- PMID: 33377130
- PMCID: PMC7762779
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100159
Epothilones Improve Axonal Growth and Motor Outcomes after Stroke in the Adult Mammalian CNS
Abstract
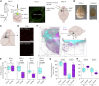
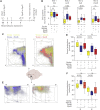
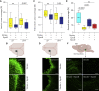
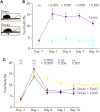
Stroke leads to the degeneration of short-range and long-range axonal connections emanating from peri-infarct tissue, but it also induces novel axonal projections. However, this regeneration is hampered by growth-inhibitory properties of peri-infarct tissue and fibrotic scarring. Here, we tested the effects of epothilone B and epothilone D, FDA-approved microtubule-stabilizing drugs that are powerful modulators of axonal growth and scar formation, on neuroplasticity and motor outcomes in a photothrombotic mouse model of cortical stroke. We find that both drugs, when administered systemically 1 and 15 days after stroke, augment novel peri-infarct projections connecting the peri-infarct motor cortex with neighboring areas. Both drugs also increase the magnitude of long-range motor projections into the brainstem and reduce peri-infarct fibrotic scarring. Finally, epothilone treatment induces an improvement in skilled forelimb motor function. Thus, pharmacological microtubule stabilization represents a promising target for therapeutic intervention with a wide time window to ameliorate structural and functional sequelae after stroke.
Keywords: axon regeneration; fibrotic scar; ischemia; neuroplasticity; stroke.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
H. Witte, A. Ertürk, F. Hellal, and F.B. filed a patent on the use of microtubule-stabilizing compounds for the treatment of lesions of CNS axons (European patent no. 1858498; European patent application EP 11 00 9155.0; US patent application 11/908,118).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protein Synthesis Inhibition in the Peri-Infarct Cortex Slows Motor Recovery in Rats.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 17;11(6):e0157859. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157859. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27314672 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic administration of epothilone D improves functional recovery of walking after rat spinal cord contusion injury.Exp Neurol. 2018 Aug;306:243-249. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.12.001. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Exp Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29223322
-
Differential effects of the cell cycle inhibitor, olomoucine, on functional recovery and on responses of peri-infarct microglia and astrocytes following photothrombotic stroke in rats.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Jul 31;18(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02208-w. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34332596 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity of cortical projections after stroke.Neuroscientist. 2003 Feb;9(1):64-75. doi: 10.1177/1073858402239592. Neuroscientist. 2003. PMID: 12580341 Review.
-
Bumetanide: A review of its neuroplasticity and behavioral effects after stroke.Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2019;37(4):397-407. doi: 10.3233/RNN-190926. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31306143 Review.
Cited by
-
Microtubule-Targeting Agents: Advances in Tubulin Binding and Small Molecule Therapy for Gliomas and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 7;26(15):7652. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157652. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microtubule Targeting Agents in Disease: Classic Drugs, Novel Roles.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 12;13(22):5650. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225650. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A missense mutation in human INSC causes peripheral neuropathy.EMBO Mol Med. 2024 May;16(5):1091-1114. doi: 10.1038/s44321-024-00062-w. Epub 2024 Apr 8. EMBO Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38589651 Free PMC article.
-
Rehabilitation enhances epothilone-induced locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury.Brain Commun. 2023 Jan 13;5(1):fcad005. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcad005. eCollection 2023. Brain Commun. 2023. PMID: 36744011 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing cortical plasticity via gabapentinoid administration promotes recovery after stroke.Brain. 2022 Jul 29;145(7):2378-2393. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac103. Brain. 2022. PMID: 35905466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zerna C., Thomalla G., Campbell B.C.V., Rha J.H., Hill M.D. Current practice and future directions in the diagnosis and acute treatment of ischaemic stroke. Lancet. 2018;392:1247–1256. - PubMed
-
- Murphy T.H., Corbett D. Plasticity during stroke recovery: from synapse to behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009;10:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Stroemer R.P., Kent T.A., Hulsebosch C.E. Neocortical neural sprouting, synaptogenesis, and behavioral recovery after neocortical infarction in rats. Stroke. 1995;26:2135–2144. - PubMed
-
- Napieralski J.A., Butler A.K., Chesselet M.F. Anatomical and functional evidence for lesion-specific sprouting of corticostriatal input in the adult rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1996;373:484–497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

