An Automated Organoid Platform with Inter-organoid Homogeneity and Inter-patient Heterogeneity
- PMID: 33377132
- PMCID: PMC7762778
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100161
An Automated Organoid Platform with Inter-organoid Homogeneity and Inter-patient Heterogeneity
Abstract
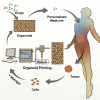
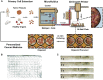
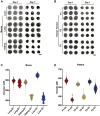
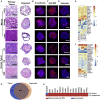
Current organoid technologies require intensive manual manipulation and lack uniformity in organoid size and cell composition. We present here an automated organoid platform that generates uniform organoid precursors in high-throughput. This is achieved by templating from monodisperse Matrigel droplets and sequentially delivering them into wells using a synchronized microfluidic droplet printer. Each droplet encapsulates a certain number of cells (e.g., 1,500 cells), which statistically represent the heterogeneous cell population in a tumor section. The system produces >400-μm organoids within 1 week with both inter-organoid homogeneity and inter-patient heterogeneity. This enables automated organoid printing to obtain one organoid per well. The organoids recapitulate 97% gene mutations in the parental tumor and reflect the patient-to-patient variation in drug response and sensitivity, from which we obtained more than 80% accuracy among the 21 patients investigated. This organoid platform is anticipated to fulfill the personalized medicine goal of 1-week high-throughput screening for cancer patients.
Keywords: droplet; microfluidics; organoid; printing; tumor.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.M., L.H., S.J., and H.Z. are listed as inventors on provisional patent applications based on components of this work.
Figures

References
-
- Dagogo-Jack I., Shaw A.T. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018;15:81–94. - PubMed
-
- Keller L., Pantel K. Unravelling tumour heterogeneity by single-cell profiling of circulating tumour cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2019;19:553–567. - PubMed
-
- Tuveson D., Clevers H. Cancer modeling meets human organoid technology. Science. 2019;364:952–955. - PubMed
-
- Jin Y., Jin K., Seung L.J., Min S., Suran K., Da-Hee A., Yun-Gon K., Seung-Woo C. Drug Screening: Vascularized Liver Organoids Generated Using Induced Hepatic Tissue and Dynamic Liver-Specific Microenvironment as a Drug Testing Platform. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018;28:1801954.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

