Omega 3 Fatty Acids and COVID-19: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 33377319
- PMCID: PMC7779984
- DOI: 10.3947/ic.2020.52.4.478
Omega 3 Fatty Acids and COVID-19: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
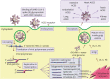
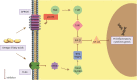
The rapid international spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 responsible for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has posed a global health emergency in 2020. It has affected over 52 million people and led to over 1.29 million deaths worldwide, as of November 13th, 2020. Patients diagnosed with COVID-19 present with symptoms ranging from none to severe and include fever, shortness of breath, dry cough, anosmia, and gastrointestinal abnormalities. Severe complications are largely due to overdrive of the host immune system leading to "cytokine storm". This results in disseminated intravascular coagulation, acute respiratory distress syndrome, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, and death. Due to its highly infectious nature and concerning mortality rate, every effort has been focused on prevention and creating new medications or repurposing old treatment options to ameliorate the suffering of COVID-19 patients including the immune dysregulation. Omega-3 fatty acids are known to be incorporated throughout the body into the bi-phospholipid layer of the cell membrane leading to the production of less pro-inflammatory mediators compared to other fatty acids that are more prevalent in the Western diet. In this article, the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids, especially eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, including their anti-inflammatory, immunomodulating, and possible antiviral effects have been discussed.
Keywords: COVID-19; Docosahexaenoic acid; Eicosapentaenoic acid; Omega-3 fatty acids; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 by The Korean Society of Infectious Diseases, Korean Society for Antimicrobial Therapy, and The Korean Society for AIDS.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hui DS, I Azhar E, Madani TA, Ntoumi F, Kock R, Dar O, Ippolito G, Mchugh TD, Memish ZA, Drosten C, Zumla A, Petersen E. The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health - The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;91:264–266. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. [Accessed 13 November 2020]. Available at: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera....
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report 26. [Accessed 13 November 2020]. Available at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

