Evaluating the relationship between quality measure adherence definitions and economic outcomes in commercial health plans: a retrospective diabetes cohort study
- PMID: 33377445
- PMCID: PMC10390994
- DOI: 10.18553/jmcp.2021.27.1.064
Evaluating the relationship between quality measure adherence definitions and economic outcomes in commercial health plans: a retrospective diabetes cohort study
Abstract
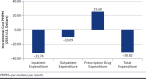
BACKGROUND: Diabetes is a prevalent chronic condition in the United States that results in considerable morbidity and mortality, frequent use of the health care system, and high health care expenditures. Adherence to antidiabetic medications can help improve health outcomes and lower health care utilization and expenditures. The Pharmacy Quality Alliance (PQA) Proportion of Days Covered (PDC): Diabetes All Class medication adherence measure was developed and endorsed to improve adherence to noninsulin antidiabetic medications; however, it has not been assessed in a commercial population of diabetes patients over a 1-year time frame. OBJECTIVE: To determine the association between adherence, as defined in the PQA medication adherence measures, and health care utilization and expenditure among commercially insured individuals using antidiabetic medications. METHODS: This 1-year retrospective study evaluated a cohort of individuals from IBM MarketScan Research Databases (2009-2015) with noninsulin antidiabetic medications. Eligible study subjects included adults (aged ≥ 18 years at index date) with continuous enrollment in their health plans for 6 months before (i.e., baseline period) and 12 months after (i.e., study period) the index date and ≥ 2 prescriptions dispensed for any medication included in the PQA PDC Diabetes All Class medication adherence measure, with at least 150 days between the first and last fill during the study period. The index date was defined as the first fill for a medication included in the PQA PDC Diabetes All Class adherence measure after a 180-day baseline period. Generalized linear models with log link and gamma distribution (expenditure) or negative binomial distribution (utilization) assessed relationships between adherence (≥ 80% PDC) and health care utilization and expenditure while adjusting for potential confounders. Cost ratios (CR) and rate ratios (RR) were computed using beta coefficients. Cohort characteristics were compared using t-tests, Wilcoxon rank sum tests, or chi-square tests with an alpha level of 0.001 set a priori. RESULTS: A total of 1,576,112 individuals were eligible; of these, 1,028,176 (65.2%) were adherent. Significant differences in demographic characteristics were observed between adherent and nonadherent groups (P < 0.001). Multivariable analyses demonstrated that adherence was associated with the following: (a) 16.6% fewer inpatient (RR = 0.834, 95% CI = 0.819-0.850) and 3.6% more outpatient service visits (RR = 1.036, 95% CI = 1.032-1.039) and (b) 16.8% lower inpatient expenditures (CR = 0.833, 95% CI = 0.829-0.836); 2.6% lower outpatient expenditures (CR = 0.974, 95% CI = 0.970-0.978); 16.4% higher prescription drug expenditures (CR = 1.164, 95% CI = 1.159-1.169); and 4.2% lower total (CR = 0.958, 95% CI = 0.954-0.962) expenditures. Adherent subjects were associated with lower incremental per member per month expenditures for inpatient (-$31.74), outpatient (-$10.09), and total (-$30.82) expenditures, yet higher prescription drug expenditures ($25.60) compared with nonadherent subjects. CONCLUSIONS: Adherence to noninsulin antidiabetic medications was associated with more outpatient and fewer inpatient visits, as well as lower total expenditures compared with nonadherence. DISCLOSURES: Funding was provided by grants from Pharmacy Quality Alliance, Merck & Co. (Kenilworth, NJ), and SinfoniaRx. In addition, Chinthammit reports personal fees from Eli Lilly and Company, outside the submitted work. Axon reports grants from the American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy and the Arizona Department of Health Services, outside the submitted work. Taylor reports grants from the Arizona Department of Health Services, outside the submitted work. Warholak reports grants from Novartis and the Arizona Department of Health Services, outside the submitted work. Chinthammit and Campbell disclose that this work was completed during their employment at the University of Arizona. This research was presented as a poster at the AMCP Annual Meeting 2019; March 25-28, 2019; San Diego, CA.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding was provided by grants from Pharmacy Quality Alliance, Merck & Co. (Kenilworth, NJ), and SinfoniaRx. In addition, Chinthammit reports personal fees from Eli Lilly and Company, outside the submitted work. Axon reports grants from the American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy and the Arizona Department of Health Services, outside the submitted work. Taylor reports grants from the Arizona Department of Health Services, outside the submitted work. Warholak reports grants from Novartis and the Arizona Department of Health Services, outside the submitted work. Chinthammit and Campbell disclose that this work was completed during their employment at the University of Arizona.
This research was presented as a poster at the AMCP Annual Meeting 2019; March 25-28, 2019; San Diego, CA.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National diabetes statistics report, 2020. Accessed December 5, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/data/statistics/national-diabetes-stat...
-
- Schectman JM, Nadkarni MM, Voss JD. The association between diabetes metabolic control and drug adherence in an indigent population. Diabetes Care. 2002;25(6):1015-21. - PubMed
-
- Krapek K, King K, Warren SS, et al. Medication adherence and associated hemoglobin A1c in type 2 diabetes. Ann Pharmacother. 2004;38(9):1357-62. - PubMed
-
- Egede LE, Gebregziabher M, Echols C, Lynch CP. Longitudinal effects of medication nonadherence on glycemic control. Ann Pharmacother. 2014;48(5):562-70. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical