Histologic progression of acne inversa/hidradenitis suppurativa: Implications for future investigations and therapeutic intervention
- PMID: 33377546
- PMCID: PMC8247901
- DOI: 10.1111/exd.14273
Histologic progression of acne inversa/hidradenitis suppurativa: Implications for future investigations and therapeutic intervention
Abstract
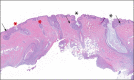
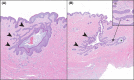
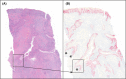
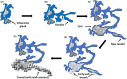
Since first recognized in 1839, the pathogenesis of acne inversa (AI) has undergone repeated revisions. Although there is agreement that AI involves occlusion of hair follicles with subsequent inflammation and the formation of tracts, the histologic progression of this disease still requires refinement. The objective of this study was to examine the histologic progression of AI based on the examination of a large cohort of punch biopsies and excisional samples that were examined first by hematoxylin and eosin staining. The most informative of these samples were step-sectioned and stained by immunohistochemistry for epithelial and inflammatory markers. Based on this examination, the following observations were made: 1) AI arises from the epithelium of the infundibulum of terminal and vellus hairs; 2) These form cysts and epithelial tendrils that extend into soft tissue; 3) Immunohistochemical staining demonstrates the epithelium of AI is disordered with infundibular and isthmic differentiation and de novo expression of stem cell markers; 4) The inflammatory response in AI is heterogeneous and largely due to cyst rupture. The conclusions of this investigation were that AI is an epithelial-driven disease caused by infiltrative, cyst forming tendrils and most of the inflammation is due to cyst rupture and release of cornified debris and bacteria. Cyst rupture often occurs below the depths of punch biopsy samples indicating their use for analysis may give an incomplete picture of the disease. Finally, our data suggest that unless therapies inhibit tendril development, it is unlikely they will cause prolonged treatment-induced remission in AI.
Keywords: Hidradenitis suppurativa; diseases; hair follicle; inflammatory skin; pathogenesis.
© 2020 Abbvie. Experimental Dermatology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Australasian Hair and Wool Research Society (AHWRS) and European Immunodermatology Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. M. Rosenblum, M. Lowe, J. Gudjonsson and P.W. Harms have served as consultants to AbbVie and have received research funding. Drs R.W. Dunstan, V. Todorović, V.E Scott, K.M. Smith, P. Honore, Ms. K.M. Salte and Mr. J.B. Wetter are employees of AbbVie.
Figures
References
-
- Hoffman LK, Ghias MH, Garg A, Hamzavi IH, Alavi A, Lowes MA. Major gaps in understanding and treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2017;36(2):86‐92. - PubMed
-
- Ralf Paus L, Kurzen H, Kurokawa I, et al. What causes hidradenitis suppurativa? Exp Dermatol. 2008;17(5):455‐456. - PubMed
-
- Alikhan A, Lynch PJ, Eisen DB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60(4):539‐561. - PubMed
-
- Yu Ca C‐W, Cook MG. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a disease of follicular epithelium, rather than apocrine glands. Br J of Dermatol. 1990;122(6):763‐769. - PubMed
-
- Prens E, Deckers I. Pathophysiology of hidradenitis suppurativa: an update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73(5):S8‐S11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

