Multimodal MRI assessment for first episode psychosis: A major change in the thalamus and an efficient stratification of a subgroup
- PMID: 33377594
- PMCID: PMC7856640
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.25276
Multimodal MRI assessment for first episode psychosis: A major change in the thalamus and an efficient stratification of a subgroup
Abstract
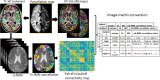
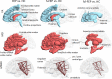
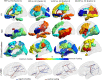
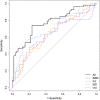
Multi-institutional brain imaging studies have emerged to resolve conflicting results among individual studies. However, adjusting multiple variables at the technical and cohort levels is challenging. Therefore, it is important to explore approaches that provide meaningful results from relatively small samples at institutional levels. We studied 87 first episode psychosis (FEP) patients and 62 healthy subjects by combining supervised integrated factor analysis (SIFA) with a novel pipeline for automated structure-based analysis, an efficient and comprehensive method for dimensional data reduction that our group recently established. We integrated multiple MRI features (volume, DTI indices, resting state fMRI-rsfMRI) in the whole brain of each participant in an unbiased manner. The automated structure-based analysis showed widespread DTI abnormalities in FEP and rs-fMRI differences between FEP and healthy subjects mostly centered in thalamus. The combination of multiple modalities with SIFA was more efficient than the use of single modalities to stratify a subgroup of FEP (individuals with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder) that had more robust deficits from the overall FEP group. The information from multiple MRI modalities and analytical methods highlighted the thalamus as significantly abnormal in FEP. This study serves as a proof-of-concept for the potential of this methodology to reveal disease underpins and to stratify populations into more homogeneous sub-groups.
Keywords: DTI; factor analysis; first-episode psychosis; multimodal MRI; resting state fMRI; schizophrenia.
© 2020 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
S. Mori and M. I. Miller own “AnatomyWorks”. Dr. Mori is its CEO. This arrangement is managed by the Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict‐of‐interest policies. All the authors have declared no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Agcaoglu, O. , Miller, R. , Damaraju, E. , Rashid, B. , Bustillo, J. , Cetin, M. S. , … Calhoun, V. D. (2017). Decreased hemispheric connectivity and decreased intra‐ and inter‐hemisphere asymmetry of resting state functional network connectivity in schizophrenia. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 12(3), 615–630. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Altamura, A. C. , Delvecchio, G. , Marotta, G. , Oldani, L. , Pigoni, A. , Ciappolino, V. , … Brambilla, P. (2017). Structural and metabolic differentiation between bipolar disorder with psychosis and substance‐induced psychosis: An integrated MRI/PET study. European Psychiatry: The Journal of the Association of European Psychiatrists, 41, 85–94. - PubMed
-
- Anticevic, A. (2017). Understanding the role of thalamic circuits in schizophrenia neuropathology. Schizophrenia Research, 180, 1–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

