Effect of Capivasertib in Patients With an AKT1 E17K-Mutated Tumor: NCI-MATCH Subprotocol EAY131-Y Nonrandomized Trial
- PMID: 33377972
- PMCID: PMC7774047
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.6741
Effect of Capivasertib in Patients With an AKT1 E17K-Mutated Tumor: NCI-MATCH Subprotocol EAY131-Y Nonrandomized Trial
Erratum in
-
Error in the Abstract.JAMA Oncol. 2021 Nov 1;7(11):1729. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.5290. JAMA Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34591077 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: In the National Cancer Institute Molecular Analysis for Therapy Choice (NCI-MATCH) trial, agents targeting genetic tumor abnormalities are administered to patients. In the NCI-MATCH subprotocol EAY131-Y trial, patients with an AKT1 E17K-mutated metastatic tumor received the pan-AKT inhibitor capivasertib.
Objective: To assess the objective response rate (ORR) of capivasertib in patients with an AKT1 E17K-mutated tumor.
Design, setting, and participants: Between July 13, 2016, and August 10, 2017, patients in the NCI-MATCH trial were enrolled and assigned to the subprotocol EAY131-Y nonrandomized trial. Patients included adults with an AKT1 E17K-mutated metastatic tumor that had progressed with standard treatment, and these patients were assigned to receive capivasertib. Tumor assessments were repeated every 2 cycles. Data analysis of this evaluable population was performed from November 8, 2019, to March 12, 2020.
Interventions: The study treatment was capivasertib, 480 mg, orally twice daily for 4 days on and 3 days off weekly in 28-day cycles until disease progression or unacceptable toxic effect. If patients continued hormone therapy for metastatic breast cancer, the capivasertib dose was 400 mg.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point was the ORR (ie, complete response [CR] and partial response) according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors criteria, version 1.1. Secondary end points included progression-free survival (PFS), 6-month PFS, overall survival, and safety.
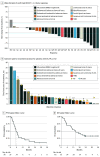
Results: In total, 35 evaluable and analyzable patients were included, of whom 30 were women (86%), and the median (range) age was 61 (32-73) years. The most prevalent cancers were breast (18 [51%]), including 15 patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive/ERBB2-negative and 3 with triple-negative disease, and gynecologic (11 [31%]) cancers. The ORR rate was 28.6% (95% CI, 15%-46%). One patient with endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma achieved a CR and remained on therapy at 35.6 months. Patients with confirmed partial response had the following tumor types: 7 had HR-positive/ERBB2-negative breast cancer, 1 had uterine leiomyosarcoma, and 1 had oncocytic parotid gland carcinoma and continued receiving treatment at 28.8 months. Sixteen patients (46%) had stable disease as the best response, 2 (6%) had progressive disease, and 7 (20%) were not evaluable. With a median follow-up of 28.4 months, the overall 6-month PFS rate was 50% (95% CI, 35%-71%). Capivasertib was discontinued because of adverse events in 11 of 35 patients (31%). Grade 3 treatment-related adverse events included hyperglycemia (8 [23%]) and rash (4 [11%]). One grade 4 hyperglycemic adverse event was reported.
Conclusions and relevance: This nonrandomized trial found that, in patients with an AKT1 E17K-mutated tumor treated with capivasertib, a clinically significant ORR was achieved, including 1 CR. Clinically meaningful activity with single-agent capivasertib was demonstrated in refractory malignant neoplasms, including rare cancers.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00700882.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

