Restriction of cytosolic sucrose hydrolysis profoundly alters development, metabolism, and gene expression in Arabidopsis roots
- PMID: 33378456
- PMCID: PMC7921298
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/eraa581
Restriction of cytosolic sucrose hydrolysis profoundly alters development, metabolism, and gene expression in Arabidopsis roots
Abstract
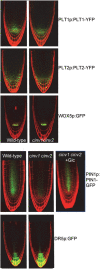
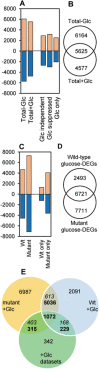
Plant roots depend on sucrose imported from leaves as the substrate for metabolism and growth. Sucrose and hexoses derived from it are also signalling molecules that modulate growth and development, but the importance for signalling of endogenous changes in sugar levels is poorly understood. We report that reduced activity of cytosolic invertase, which converts sucrose to hexoses, leads to pronounced metabolic, growth, and developmental defects in roots of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) seedlings. In addition to altered sugar and downstream metabolite levels, roots of cinv1 cinv2 mutants have reduced elongation rates, cell and meristem size, abnormal meristematic cell division patterns, and altered expression of thousands of genes of diverse functions. Provision of exogenous glucose to mutant roots repairs relatively few of the defects. The extensive transcriptional differences between mutant and wild-type roots have hallmarks of both high sucrose and low hexose signalling. We conclude that the mutant phenotype reflects both low carbon availability for metabolism and growth and complex sugar signals derived from elevated sucrose and depressed hexose levels in the cytosol of mutant roots. Such reciprocal changes in endogenous sucrose and hexose levels potentially provide rich information about sugar status that translates into flexible adjustments of growth and development.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; hexose; neutral invertase; root; root transcriptome; sucrose; sugar signalling.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Figures


References
-
- Aida M, Beis D, Heidstra R, Willemsen V, Blilou I, Galinha C, Nussaume L, Noh YS, Amasino R, Scheres B. 2004. The PLETHORA genes mediate patterning of the Arabidopsis root stem cell niche. Cell 119, 109–120. - PubMed
-
- Baena-González E, Hanson J. 2017. Shaping plant development through the SnRK1–TOR metabolic regulators. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 35, 152–157. - PubMed
-
- Baena-González E, Lunn JE. 2020. SnRK1 and trehalose 6-phosphate—two ancient pathways converge to regulate plant metabolism and growth. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 55, 52–59. - PubMed
-
- Barnes WJ, Anderson CT. 2018. Cytosolic invertases contribute to cellulose biosynthesis and influence carbon partitioning in seedlings of Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Journal 94, 956–974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BBS/E/J/00000020/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/J/000PR9790/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/I01280X/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J004561/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

