Accelerative effect of topical Zataria multiflora essential oil against infected wound model by modulating inflammation, angiogenesis, and collagen biosynthesis
- PMID: 33378625
- PMCID: PMC7782911
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1861029
Accelerative effect of topical Zataria multiflora essential oil against infected wound model by modulating inflammation, angiogenesis, and collagen biosynthesis
Abstract
Context: Zataria multiflora Boiss (Lamiaceae) essential oil (ZME) is believed to be a bactericide herbal medicine and might alleviate negative effects of infection.
Objective: This study evaluates the effects of an ointment prepared from ZME (ZMEO) on infected wounds.
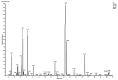
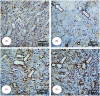
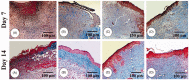
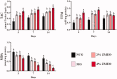
Materials and methods: A full-thickness excisional skin wound was surgically created in each mouse and inoculated with 5 × 107 suspension containing Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. The BALB/c mice (n = 72) were divided into four groups: (1) negative control that received base ointment (NCG), (2) positive control that daily received Mupirocin® (MG), (3) therapeutic ointment containing 2% ZMEO and (4) therapeutic ointment containing 4% ZMEO, for 21 days. Wound contraction, total bacterial count, histopathological parameters, antioxidant activity, qRT-PCR analysis for expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, VEGF, IGF-1, TGF-β, IL-10, and FGF-2 mRNA levels were assessed on days 3, 7, and 14 following the wounding.
Results: Topical administration of ZMEO significantly decreased the total bacterial count and wound area and also expression of IL-1β and TNF-α compared to the control groups (p < 0.05) in all days. This could also increase significantly the expression of TGF-β, IL-10 IGF-1, FGF-2, and VEGF, and also angiogenesis, fibroblasts, fibrocytes, epithelialization ratio, and collagen deposition and improve antioxidant status compared to the control group (p < 0.05).
Discussion and conclusion: ZMEO accelerated the healing process of infected wounds by shortening the inflammatory factors and increasing proliferative phase. Applying ZMEO only and/or in combination with chemical agents for the treatment of wound healing could be suggested.
Keywords: Infected wound healing; antimicrobial properties; inflammatory cytokines; thymol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Accelerated healing by topical administration of Salvia officinalis essential oil on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus infected wound model.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Aug;128:110120. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110120. Epub 2020 May 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32460189
-
Effectiveness of topical administration of Anethum graveolens essential oil on MRSA-infected wounds.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jan;109:1650-1658. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.117. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30551419
-
Topical Administration of an Ointment Prepared From Satureja sahendica Essential Oil Accelerated Infected Full-Thickness Wound Healing by Modulating Inflammatory Response in a Mouse Model.Wounds. 2021 Dec;33(12):321-328. Wounds. 2021. PMID: 34882574
-
[The modern approach to wound treatment].Med Pregl. 2000 Jul-Aug;53(7-8):363-8. Med Pregl. 2000. PMID: 11214479 Review. Croatian.
-
Effects of Carvacrol, Thymol and essential oils containing such monoterpenes on wound healing: a systematic review.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019 Feb;71(2):141-155. doi: 10.1111/jphp.13054. Epub 2018 Dec 7. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30537169
Cited by
-
Effects of irradiated biological dressings on second-degree burn wounds.Afr Health Sci. 2023 Jun;23(2):367-373. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v23i2.41. Afr Health Sci. 2023. PMID: 38223637 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of PCL nanofiber mats coated with chitosan microcapsules containing cinnamon essential oil for wound healing.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Mar 18;23(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03905-0. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 36934283 Free PMC article.
-
Platycodin D inhibits the proliferation and migration of hypertrophic scar-derived fibroblasts and promotes apoptosis through a caspase-dependent pathway.Arch Dermatol Res. 2023 Jul;315(5):1257-1267. doi: 10.1007/s00403-022-02513-1. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023. PMID: 36526799 Free PMC article.
-
The histological assessment of new bone formation with zolendronic acid loaded bone allograft in rabbit femoral bone defect.J Med Life. 2023 Apr;16(4):616-622. doi: 10.25122/jml-2022-0314. J Med Life. 2023. PMID: 37305828 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and innovations in treating chronic and acute wound infections: from basic science to clinical practice.Burns Trauma. 2022 May 21;10:tkac014. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkac014. eCollection 2022. Burns Trauma. 2022. PMID: 35611318 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams RP. 2007. Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. 4th ed. Carol Stream (IL): Allured Publishing Corporation.
-
- Aghdam SY, Eming SA, Willenborg S, Neuhaus B, Niessen CM, Partridge L, Krieg T, Bruning JC.. 2012. Vascular endothelial insulin/IGF-1 signaling controls skin wound vascularization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 421(2):197–202. - PubMed
-
- Aida A, Ali MS, Behrooz MV.. 2015. Chemical composition and antimicrobial effect of the essential oil of Zataria multiflora Boiss endemic in Khorasan-Iran. Asian Pac J Trop Dis. 5(3):181–185.
-
- Bardaa S, Moalla D, Ben Khedir S, Rebai T, Sahnoun Z.. 2016. The evaluation of the healing proprieties of pumpkin and linseed oils on deep second-degree burns in rats. Pharm Biol. 54(4):581–587. - PubMed
-
- Barkhori-Mehni S, Khanzadi S, Hashemi M, Azizzadeh M, 2017. Antibacterial activity of Zataria multiflora Boiss essential oil against some fish spoilage bacteria. J Hum Environ Health Promot. 2(4):220–225.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
