Alterations in Rat Accumbens Dopamine, Endocannabinoids and GABA Content During WIN55,212-2 Treatment: The Role of Ghrelin
- PMID: 33379212
- PMCID: PMC7795825
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22010210
Alterations in Rat Accumbens Dopamine, Endocannabinoids and GABA Content During WIN55,212-2 Treatment: The Role of Ghrelin
Abstract
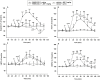
The endocannabinoid/CB1R system as well as the central ghrelin signalling with its growth hormone secretagogoue receptors (GHS-R1A) are importantly involved in food intake and reward/reinforcement processing and show distinct overlaps in distribution within the relevant brain regions including the hypothalamus (food intake), the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and the nucleus accumbens (NAC) (reward/reinforcement). The significant mutual interaction between these systems in food intake has been documented; however, the possible role of ghrelin/GHS-R1A in the cannabinoid reinforcement effects and addiction remain unclear. Therefore, the principal aim of the present study was to investigate whether pretreatment with GHS-R1A antagonist/JMV2959 could reduce the CB1R agonist/WIN55,212-2-induced dopamine efflux in the nucleus accumbens shell (NACSh), which is considered a crucial trigger impulse of the addiction process. The synthetic aminoalklylindol cannabinoid WIN55,212-2 administration into the posterior VTA induced significant accumbens dopamine release, which was significantly reduced by the 3 mg/kg i.p. JMV2959 pretreatment. Simultaneously, the cannabinoid-increased accumbens dopamine metabolic turnover was significantly augmented by the JMV2959 pretreament. The intracerebral WIN55,212-2 administration also increased the endocannabinoid arachidonoylethanolamide/anandamide and the 2-arachidonoylglycerol/2-AG extracellular levels in the NACSh, which was moderately but significantly attenuated by the JMV2959 pretreatment. Moreover, the cannabinoid-induced decrease in accumbens γ-aminobutyric acid/gamma-aminobutyric acid levels was reversed by the JMV2959 pretreatment. The behavioural study in the LABORAS cage showed that 3 mg/kg JMV2959 pretreatment also significantly reduced the systemic WIN55,212-2-induced behavioural stimulation. Our results demonstrate that the ghrelin/GHS-R1A system significantly participates in the rewarding/reinforcing effects of the cannabinoid/CB1 agonist that are involved in cannabinoid addiction processing.
Keywords: 2-arachidonoylglycerol/2-AG; GABA; addiction; anandamide/AEA; dopamine; dopamine metabolism; endocannabinoids; ghrelin/GHS-R1A; nucleus accumbens shell microdialysis; synthetic cannabinoid WIN55,212-2.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

