Performance of a Point-of-Care Test for the Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen
- PMID: 33379279
- PMCID: PMC7823488
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9010058
Performance of a Point-of-Care Test for the Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen
Abstract
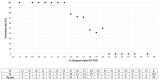
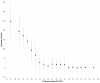
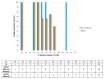
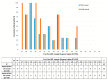
The rapid detection of infections caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is necessary in the ongoing pandemic. Antigen-specific point-of-care tests (POCT) may be useful for this purpose. Here, such a POCT (SARS-CoV-2 NADAL® COVID-19 Ag) was compared to a laboratory-developed triplex real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) designed for the detection of viral nucleoprotein gene and two control targets. This RT-PCR served as a reference to investigate POCT sensitivity by re-testing upper respiratory tract (URT) samples (n = 124) exhibiting different SARS-CoV-2 loads in terms of RT-PCR threshold cycle (Ct) values. The optical intensities of the antigen bands were compared to the Ct values of the RT-PCR. The infectivity of various virus loads was estimated by inoculating Vero cells with URT samples (n = 64, Ct 17-34). POCT sensitivity varied from 100% (Ct < 25) to 73.1% (Ct ≤ 30); higher SARS-CoV-2 loads correlated with higher band intensities. All samples with a Ct > 30 were negative; among SARS-CoV-2 free samples (n = 10) no false-positives were detected. A head-to-head comparison with another POCT (Abbott, Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test) yielded similar results. Isolation of SARS-CoV-2 in cell-culture was successful up to a Ct value of 29. The POCT reliably detects high SARS-CoV-2 loads and rapidly identifies infectious individuals.
Keywords: COVID-19; PCR; POCT; antigen; comparison; diagnostic.
Conflict of interest statement
As already mentioned in the material and methods section, some samples were filled with PBS after testing and made available for a further study on the suitability of SARS-CoV-2 antigen assays. Therefore, these samples have a lower antigen concentration and can be viewed and examined as new samples. We therefore consider it justified keeping these samples in our study and to present the results. The authors declare no conflict of interest. The Nal von Minden GmbH supported this study by providing free kits and a scanner for optical intensity measurement. This company had no influence on the writing of the manuscript or on the interpretation of the data.
Figures

References
-
- Payan C., Ducancelle A., Aboubaker M.H., Caer J., Tapia M., Chauvin A., Peyronnet D., Le Hen E., Arab Z., Legrand M.-C., et al. Human Papillomavirus Quantification in Urine and Cervical Samples by Using the Mx4000 and LightCycler General Real-Time PCR Systems. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007;45:897–901. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02022-06. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

