Developing a theoretical evolutionary framework to solve the mystery of parturition initiation
- PMID: 33380346
- PMCID: PMC7775106
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.58343
Developing a theoretical evolutionary framework to solve the mystery of parturition initiation
Abstract
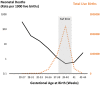
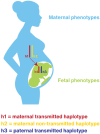
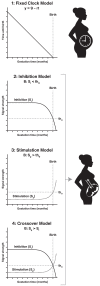
Eutherian mammals have characteristic lengths of gestation that are key for reproductive success, but relatively little is known about the processes that determine the timing of parturition, the process of birth, and how they are coordinated with fetal developmental programs. This issue remains one of biology's great unsolved mysteries and has significant clinical relevance because preterm birth is the leading cause of infant and under 5 year old child mortality worldwide. Here, we consider the evolutionary influences and potential signaling mechanisms that maintain or end pregnancy in eutherian mammals and use this knowledge to formulate general theoretical evolutionary models. These models can be tested through evolutionary species comparisons, studies of experimental manipulation of gestation period and birth timing, and human clinical studies. Understanding how gestation time and parturition are determined will shed light on this fundamental biological process and improve human health through the development of therapies to prevent preterm birth.
Keywords: eutherian mammals; evolution; evolutionary biology; medicine; parturition; pregnancy; prematurity; preterm birth.
© 2020, Rokas et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AR Reviewing editor, eLife, SM, OT, AL, GZ No competing interests declared, LM is currently President and CEO of the Burroughs Wellcome Fund. The content of this article does not convey the opinion of the Burroughs Wellcome Fund.
Figures


References
-
- Aghaeepour N, Ganio EA, Mcilwain D, Tsai AS, Tingle M, Van Gassen S, Gaudilliere DK, Baca Q, McNeil L, Okada R, Ghaemi MS, Furman D, Wong RJ, Winn VD, Druzin ML, El-Sayed YY, Quaintance C, Gibbs R, Darmstadt GL, Shaw GM, Stevenson DK, Tibshirani R, Nolan GP, Lewis DB, Angst MS, Gaudilliere B. An immune clock of human pregnancy. Science Immunology. 2017;2:eaan2946. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aan2946. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen WM. Physiology of the corpus luteum VI. the production of progestational proliferation of the endometrium of the mature rabbit by progestin (an extract of the corpus luteum) after preliminary treatment with oestrin. American Journal of Physiology. 1930;92:612–681. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1930.92.3.612. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

