Inhibition of Efferocytosis by Extracellular CIRP-Induced Neutrophil Extracellular Traps
- PMID: 33380498
- PMCID: PMC7854515
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000091
Inhibition of Efferocytosis by Extracellular CIRP-Induced Neutrophil Extracellular Traps
Abstract
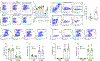
Phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells by the macrophages (efferocytosis) is impaired in sepsis, but its mechanism is poorly understood. Extracellular cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (eCIRP) is a novel damage-associated molecular pattern that fuels inflammation. We identify that eCIRP-induced neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) impair efferocytosis through a novel mechanism. Coculture of macrophages and apoptotic thymocytes in the presence of recombinant murine CIRP (rmCIRP)-induced NETs significantly inhibited efferocytosis. Efferocytosis was significantly inhibited in the presence of rmCIRP-treated wild-type (WT), but not PAD4-/- neutrophils. Efferocytosis in the peritoneal cavity of rmCIRP-injected PAD4-/- mice was higher than WT mice. Milk fat globule-EGF-factor VIII (MFG-E8), an opsonin, increased macrophage efferocytosis, whereas the inhibition of efferocytosis by NETs was not rescued upon addition of MFG-E8, indicating disruption of MFG-E8's receptor(s) αvβ3 or αvβ5 integrin by the NETs. We identified neutrophil elastase in the NETs significantly inhibited efferocytosis by cleaving macrophage surface integrins αvβ3 and αvβ5 Using a preclinical model of sepsis, we found that CIRP-/- mice exhibited significantly increased rate of efferocytosis in the peritoneal cavity compared with WT mice. We discovered a novel role of eCIRP-induced NETs to inhibit efferocytosis by the neutrophil elastase-dependent decrease of αvβ3/αvβ5 integrins in macrophages. Targeting eCIRP ameliorates sepsis by enhancing efferocytosis.
Copyright © 2021 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures





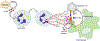
References
-
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, Martin GS, Opal SM, Rubenfeld GD, van der Poll T, Vincent JL, and Angus DC. 2016. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 315: 801–810. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wesche DE, Lomas-Neira JL, Perl M, Chung CS, and Ayala A. 2005. Leukocyte apoptosis and its significance in sepsis and shock. J Leukoc Biol 78: 325–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

