New 'Antigens' in Membranous Nephropathy
- PMID: 33380523
- PMCID: PMC8054892
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2020071082
New 'Antigens' in Membranous Nephropathy
Abstract
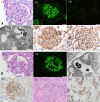
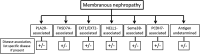
Membranous nephropathy (MN) occurs due to deposition of immune complexes along the subepithelial region of glomerular basement membrane. Two previously identified target antigens for the immune complexes, PLA2R (identified in 2009) and THSD7A (in 2014), account for approximately 60% of all MN, both primary and secondary. In the remaining MN, target antigens were unknown. Use of laser microdissection and mass spectrometry enabled identification of new "antigens." This approach led to the identification of four novel types of MN: exotosin 1 (EXT1)- and exotosin 2 (EXT2)-associated MN, NELL1-associated MN, Sema3B-associated MN, and PCDH7-associated MN. Each of these represents a distinct disease entity, with different clinical and pathologic findings. In this review, the structure of the proteins and the clinical and pathologic findings of the new types of MN are discussed. The role of mass spectrometry for accurate diagnosis of MN cannot be overemphasized. Finally, any classification of MN should be made on the basis of the antigens that are detected. Further studies are required to understand the pathophysiology, response to treatment, and outcomes of these new MNs.
Keywords: kidney biopsy; membranous nephropathy; nephrotic syndrome.
Copyright © 2021 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures




References
-
- Heymann W, Hackel DB, Harwood S, Wilson SG, Hunter JL: Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund’s adjuvants and rat kidney suspensions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 100: 660–664, 1959 - PubMed
-
- Sethi S, Theis JD: Pathology and diagnosis of renal non-AL amyloidosis. J Nephrol 31: 343–350, 2018 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

