Acylated Ghrelin as a Multi-Targeted Therapy for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 33381011
- PMCID: PMC7767977
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2020.614828
Acylated Ghrelin as a Multi-Targeted Therapy for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
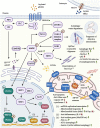
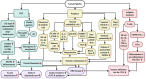
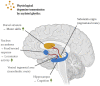
Much thought has been given to the impact of Amyloid Beta, Tau and Alpha-Synuclein in the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD), yet the clinical failures of the recent decades indicate that there are further pathological mechanisms at work. Indeed, besides amyloids, AD and PD are characterized by the culminative interplay of oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and hyperfission, defective autophagy and mitophagy, systemic inflammation, BBB and vascular damage, demyelination, cerebral insulin resistance, the loss of dopamine production in PD, impaired neurogenesis and, of course, widespread axonal, synaptic and neuronal degeneration that leads to cognitive and motor impediments. Interestingly, the acylated form of the hormone ghrelin has shown the potential to ameliorate the latter pathologic changes, although some studies indicate a few complications that need to be considered in the long-term administration of the hormone. As such, this review will illustrate the wide-ranging neuroprotective properties of acylated ghrelin and critically evaluate the hormone's therapeutic benefits for the treatment of AD and PD.
Keywords: autophagy; dopamine; ghrelin; growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1 alpha; inflammation; insulin resistance; mitochondrial dysfunction; neurodegeneration.
Copyright © 2020 Reich and Hölscher.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
-
The neuroprotective effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease: An in-depth review.Front Neurosci. 2022 Sep 1;16:970925. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.970925. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36117625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From cradle to grave: neurogenesis, neuroregeneration and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.Neural Regen Res. 2022 Dec;17(12):2606-2614. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.336138. Neural Regen Res. 2022. PMID: 35662189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amyloid Beta and Phosphorylated Tau-Induced Defective Autophagy and Mitophagy in Alzheimer's Disease.Cells. 2019 May 22;8(5):488. doi: 10.3390/cells8050488. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31121890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acylated but not des-acyl ghrelin is neuroprotective in an MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease.J Neurochem. 2016 May;137(3):460-71. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13576. Epub 2016 Mar 11. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 26872221 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Changes in Circulating Acylated Ghrelin and Neutrophil Elastase in Diabetic Retinopathy.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jan 8;60(1):118. doi: 10.3390/medicina60010118. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38256379 Free PMC article.
-
"Sibling" battle or harmony: crosstalk between nesfatin-1 and ghrelin.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Mar 3;79(3):169. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04193-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35239020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Relevance of Ghrelin in Programmed Cell Death and Its Application in Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 8;24(24):17254. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417254. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ghrelin as a Biomarker of "Immunometabolic Depression" and Its Connection with Dysbiosis.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 13;15(18):3960. doi: 10.3390/nu15183960. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ghrelin, Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Mood Disorders: What Are the Connections?Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025;23(2):172-186. doi: 10.2174/1570159X22999240722095039. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39041263 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams B. (2020). Roche, AC Immune's Tau-Blocking Drug Flops in Alzheimer's as Biotech's Shares Halved. Available online at: https://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/roche-ac-immune-s-tau-blocking-dru... (accessed Octobar 01, 2020).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

