A Combined Phytochemistry and Network Pharmacology Approach to Reveal the Effective Substances and Mechanisms of Wei-Fu-Chun Tablet in the Treatment of Precancerous Lesions of Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 33381024
- PMCID: PMC7768900
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.558471
A Combined Phytochemistry and Network Pharmacology Approach to Reveal the Effective Substances and Mechanisms of Wei-Fu-Chun Tablet in the Treatment of Precancerous Lesions of Gastric Cancer
Abstract
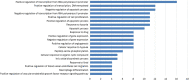
Wei-Fu-Chun (WFC) tablet is a commercial medicinal product approved by China Food and Drug Administration, which is made of Panax ginseng C.A.Mey., Citrus aurantium L., and Isodon amethystoides (Benth.). WFC has been popularly used for the treatment of precancerous lesions of gastric cancer (PLGC) in clinical practice. In this study, a UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF/MS method in both positive and negative ion mode was employed to rapidly survey the major constituents of WFC. 178 compounds including diterpenoids, triterpenes, sesquiterpenes, flavonoids, saponins, phenylpropanoids, lignans, coumarins, organic acids, fatty acids, quinones, and sterols, were identified by comparing their retention times, accurate mass within 5 ppm error, and MS fragmentation ions. In addition, 77 absorbed parent molecules and nine metabolites in rat serum were rapidly characterized by UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF/MS. The network pharmacology method was used to predict the active components, corresponding therapeutic targets, and related pathways of WFC in the treatment of PLGC. Based on the main compounds in WFC and their metabolites in rat plasma and existing databases, 13 active components, 48 therapeutic targets, and 61 pathways were found to treat PLGC. The results of PLGC experiment in rats showed that WFC could improve the weight of PLGC rats and the histopathological changes of gastric mucosa partly by inhibiting Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway to increase pepsin secretion. This study offers an applicable approach to identify chemical components, absorbed compounds, and metabolic compounds in WFC, and provides a method to explore bioactive ingredients and action mechanisms of WFC.
Keywords: UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF/MS; Wei-Fu-Chun tablet; effective substances and mechanism; network pharmacology; precancerous lesions of gastric cancer.
Copyright © 2020 Wang, Wu, Xie, Ding, Lv, Bian, Chen, Nisma Lena, Wang, Ye and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
HW, RW, XL, KL and GY were employed by Shangai Pharmaceuticals Holding Co., Ltd.. LD was employed by Shanghai Zhonghua Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd. WC were employed by Huqingyutang Chinese Medicine Medernization Research Institute of Zhejiang Province. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Dan M., Xie G., Gao X., Long X., Su M., Zhao A., et al. (2009). A rapid ultra-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray Ionisation mass spectrometric method for the analysis of saponins in the adventitious roots of Panax notoginseng. Phytochem. Anal. 20 (1), 68–76. 10.1002/pca.1099 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Díaz-Serrano A., Angulo B., Dominguez C., Pazo-Cid R., Salud A., Jiménez-Fonseca P., et al. (2018). Genomic profiling of HER2-positive gastric cancer: PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as predictor of outcomes in HER2-positive advanced gastric cancer treated with trastuzumab. Oncologist 23 (9), 1092–1102. 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0379 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

