Antimicrobial Resistance and in silico Virulence Profiling of Aliarcobacter butzleri Strains From German Water Poultry
- PMID: 33381106
- PMCID: PMC7767855
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.617685
Antimicrobial Resistance and in silico Virulence Profiling of Aliarcobacter butzleri Strains From German Water Poultry
Abstract
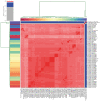
Aliarcobacter butzleri is an emerging foodborne and zoonotic pathogen that is usually transmitted via contaminated food or water. A. butzleri is not only the most prevalent Aliarcobacter species, it is also closely related to thermophilic Campylobacter, which have shown increasing resistance in recent years. Therefore, it is important to assess its resistance and virulence profiles. In this study, 45 Aliarcobacter butzleri strains from water poultry farms in Thuringia, Germany, were subjected to an antimicrobial susceptibility test using the gradient strip diffusion method and whole-genome sequencing. In the phylogenetic analysis, the genomes of the German strains showed high genetic diversity. Thirty-three isolates formed 11 subgroups containing two to six strains. The antimicrobial susceptibility testing showed that 32 strains were resistant to erythromycin, 26 to doxycycline, and 20 to tetracycline, respectively. Only two strains were resistant to ciprofloxacin, while 39 strains were resistant to streptomycin. The in silico prediction of the antimicrobial resistance profiles identified a large repertoire of potential resistance mechanisms. A strong correlation between a gyrA point mutation (Thr-85-Ile) and ciprofloxacin resistance was found in 11 strains. A partial correlation was observed between the presence of the bla3 gene and ampicillin resistance. In silico virulence profiling revealed a broad spectrum of putative virulence factors, including a complete lipid A cluster in all studied genomes.
Keywords: Aliarcobacter; antibiotic susceptibility; antimicrobial resistance; emerging pathogen; heavy metal resistance; virulence; whole-genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2020 Müller, Hotzel, Linde, Hänel and Tomaso.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abdelbaqi K., Menard A., Prouzet-Mauleon V., Bringaud F., Lehours P., Megraud F. (2007). Nucleotide sequence of the gyrA gene of Arcobacter species and characterization of human ciprofloxacin-resistant clinical isolates. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 49, 337–345. 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2006.00208.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

