The Expression and Prognostic Value of FGF2, FGFR3, and FGFBP1 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 33381388
- PMCID: PMC7748917
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2872479
The Expression and Prognostic Value of FGF2, FGFR3, and FGFBP1 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma was treated by operation and chemoradiotherapy. However, the prognosis of most patients is poor after treatment, and most studies have shown that FGF2 and its receptor (FGFR) are involved in the development of various malignant tumors. FGF2 plays an important role in tumor progression and malignancy. In this study, the immunohistochemistry of FGF2, FGFR3, and FGFBP1 was used to further verify the expression of the three proteins in 172 patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) who had not received preoperative chemoradiotherapy and its effect on the prognosis of ESCC.
Methods: (1) χ 2 test was used to analyze the relationship between proteins and clinicopathological parameters. Survival analysis was used to investigate the effect of three proteins on prognosis. (2) Paired sample t-test was used to analyze the mRNA expression of the three proteins in fresh ESCC tissues and adjacent normal tissues.
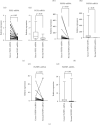
Results: FGF2 was correlated with tumor size (p = 0.026), gender (p = 0.047), and lymph metastasis (p = 0.007) in ESCC tissues. The high expression of FGFR3 was associated with tumor differentiation (p = 0.043 and p < 0.05), lymph node metastasis (p = 0.078 and p < 0.1), and race (p = 0.033 and p < 0.05). The high expression of FGFBP1 was significantly associated with the degree of tumor differentiation (p = 0.012), age (p = 0.045), and lymph node metastasis (p = 0.032) of ESCC patients. The expression of FGF2, FGFR3, and FGFBP1-mRNA in ESCC tissues was significantly higher than that in adjacent tissues (p < 0.001, p < 0.001, and p = 0.001). Patients with high expression of FGF2, FGFBP1, and FGFR3 had poor prognosis. There was a weak positive correlation between FGF2 and FGFBP1, as well as FGFR.
Conclusion: The FGF2-FGFR3 axis may promote the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The FGF2-FGFR3 axis may be a new direction of targeted therapy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. FGF2 and FGFR3 may be used as prognostic markers of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Copyright © 2020 Wenjing Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Regulation of Hippo/YAP signaling and Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma progression by an E3 ubiquitin ligase PARK2.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 25;10(21):9443-9457. doi: 10.7150/thno.46078. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32863938 Free PMC article.
-
Low expression of PRDM5 predicts poor prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jul 7;22(1):745. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09787-8. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35799142 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of YAP1 and TAZ in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Jul 16;100(28):e26597. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026597. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34260541 Free PMC article.
-
TP53 Mutations in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Sep 24;28(9):219. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2809219. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 37796679 Review.
-
The Molecular Characterization of Genetic Abnormalities in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma May Foster the Development of Targeted Therapies.Curr Oncol. 2023 Jan 3;30(1):610-640. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30010048. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36661697 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential mechanism of inhibitory effect of "medicine food homology" curcumin and its analogue EF24 on oral squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Transl Oncol. 2025 May 2. doi: 10.1007/s12094-025-03871-8. Online ahead of print. Clin Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40314923
-
Role of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor in Cancer: Biological Activity, Targeted Therapies, and Prognostic Value.Cells. 2023 Mar 24;12(7):1002. doi: 10.3390/cells12071002. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scientific Research Directions on the Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry of the Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Scientometric Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Oct 13;58(10):1449. doi: 10.3390/medicina58101449. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36295609 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting the Molecular Basis of Oesophageal Cancer for Targeted Therapies and Biomarkers for Drug Response: Guiding Clinical Decision-Making.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 22;10(10):2359. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102359. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive multi-omics analysis and prognostic significance of fibroblast growth factor binding protein 1 (FGFBP1) in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Aug 15;16(8):4101-4119. doi: 10.62347/NCRX9798. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39262727 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

