Promotion of vascular integrity in sepsis through modulation of bioactive adrenomedullin and dipeptidyl peptidase 3
- PMID: 33381880
- PMCID: PMC8246835
- DOI: 10.1111/joim.13220
Promotion of vascular integrity in sepsis through modulation of bioactive adrenomedullin and dipeptidyl peptidase 3
Abstract
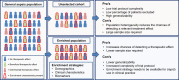
Sepsis represents one of the major medical challenges of the 21st century. Despite substantial improvements in the knowledge on pathophysiological mechanisms, this has so far not translated into novel adjuvant treatment strategies for sepsis. In sepsis, both vascular tone and vascular integrity are compromised, and contribute to the development of shock, which is strongly related to the development of organ dysfunction and mortality. In this review, we focus on dipeptidyl peptidase 3 (DPP3) and adrenomedullin (ADM), two molecules that act on the vasculature and are involved in the pathophysiology of sepsis and septic shock. DPP3 is an ubiquitous cytosolic enzyme involved in the degradation of several important signalling molecules essential for regulation of vascular tone, including angiotensin II. ADM is a key hormone involved in the regulation of vascular tone and endothelial barrier function. Previous studies have shown that circulating concentrations of both DPP3 and ADM are independently associated with the development of organ failure and adverse outcome in sepsis. We now discuss new evidence illustrating that these molecules indeed represent two distinct pathways involved in the development of septic shock. Recently, both ADM-enhancing therapies aimed at improving endothelial barrier function and vascular tone and DPP3-blocking therapies aimed at restoring systemic angiotensin responses have been shown to improve outcome in various preclinical sepsis models. Given the current lack of effective adjuvant therapies in sepsis, additional research on the therapeutic application of these peptides in humans is highly warranted.
Keywords: cardiovascular regulation; endothelial function; sepsis; vascular disease.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Internal Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Association for Publication of The Journal of Internal Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
PP received travel and consultancy reimbursement from Adrenomed and 4TEEN4, the companies that produced the ADM and DPP3 bio‐assays and antibodies described. The other authors declare no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The value of bioactive adrenomedullin and dipeptidyl peptidase 3 to predict short-term unfavourable outcomes after cardiac surgery: A prospective cohort study.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2022 Apr 1;39(4):342-351. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000001662. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 35102040
-
Adrenomedullin and Adrenomedullin-Targeted Therapy As Treatment Strategies Relevant for Sepsis.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 19;9:292. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00292. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29520277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating Biologically Active Adrenomedullin (bio-ADM) Predicts Hemodynamic Support Requirement and Mortality During Sepsis.Chest. 2017 Aug;152(2):312-320. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2017.03.035. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Chest. 2017. PMID: 28411114 Clinical Trial.
-
Monitoring circulating dipeptidyl peptidase 3 (DPP3) predicts improvement of organ failure and survival in sepsis: a prospective observational multinational study.Crit Care. 2021 Feb 15;25(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03471-2. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33588925 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of dipeptidyl peptidase 3 in pathophysiology.FEBS J. 2023 May;290(9):2246-2262. doi: 10.1111/febs.16429. Epub 2022 Mar 25. FEBS J. 2023. PMID: 35278345 Review.
Cited by
-
Alternatives to norepinephrine in septic shock: Which agents and when?J Intensive Med. 2022 Jun 12;2(4):223-232. doi: 10.1016/j.jointm.2022.05.001. eCollection 2022 Oct. J Intensive Med. 2022. PMID: 36788938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and Hypoxia as Potential Mediators of Pain in Fabry Disease: A Human-Murine Translational Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 21;24(20):15422. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015422. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895103 Free PMC article.
-
Postoperative bioactive adrenomedullin is associated with the onset of ARDS and adverse outcomes in patients undergoing open thoracoabdominal aortic surgery.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 4;14(1):12795. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63412-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38834580 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Inflammatory Biomarkers Among Patients with Sepsis of Gram-Negative Bacteria: A Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Aug 31;16:3963-3976. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S415200. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 37670930 Free PMC article.
-
Extending the 'host response' paradigm from sepsis to cardiogenic shock: evidence, limitations and opportunities.Crit Care. 2023 Nov 27;27(1):460. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04752-8. Crit Care. 2023. PMID: 38012789 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gaieski DF, Edwards JM, Kallan MJ, Carr BG. Benchmarking the incidence and mortality of severe sepsis in the United States. Crit Care Med 2021; 41: 1167–74. - PubMed
-
- Angus DC, van der Poll T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. New England J Med 2013; 369: 2063. - PubMed
-
- Abraham E, Singer M. Mechanisms of sepsis‐induced organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med 2007; 35: 2408–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

