Peripheral inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption: effects and mechanisms
- PMID: 33381913
- PMCID: PMC7804893
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.13569
Peripheral inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption: effects and mechanisms
Abstract
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is an important physiological barrier that separates the central nervous system (CNS) from the peripheral circulation, which contains inflammatory mediators and immune cells. The BBB regulates cellular and molecular exchange between the blood vessels and brain parenchyma. Normal functioning of the BBB is crucial for the homeostasis and proper function of the brain. It has been demonstrated that peripheral inflammation can disrupt the BBB by various pathways, resulting in different CNS diseases. Recently, clinical research also showed CNS complications following SARS-CoV-2 infection and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy, which both lead to a cytokine storm in the circulation. Therefore, elucidation of the mechanisms underlying the BBB disruption induced by peripheral inflammation will provide an important basis for protecting the CNS in the context of exacerbated peripheral inflammatory diseases. In the present review, we first summarize the physiological properties of the BBB that makes the CNS an immune-privileged organ. We then discuss the relevance of peripheral inflammation-induced BBB disruption to various CNS diseases. Finally, we elaborate various factors and mechanisms of peripheral inflammation that disrupt the BBB.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; central nervous system; inflammation; inflammatory factors; molecular mechanism.
© 2020 The Authors. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
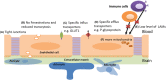
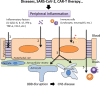
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81771293/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- JCYJ20170413165705083/Science and Technology Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality
- JCYJ20200109114608075/Science and Technology Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality
- SGLH20180625142404672/Science and Technology Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality
- 172644KYSB20200045/International collaboration project of Chinese Academy of Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

