Peptide-Drug Conjugates with Different Linkers for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 33382619
- PMCID: PMC8610607
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01530
Peptide-Drug Conjugates with Different Linkers for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
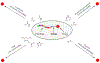
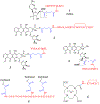
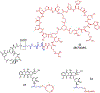
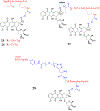
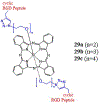
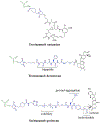
Drug conjugates are chemotherapeutic or cytotoxic agents covalently linked to targeting ligands such as an antibody or a peptide via a linker. While antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are now clinically established for cancer therapy, peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs) are gaining recognition as a new modality for targeted drug delivery with improved efficacy and reduced side effects for cancer treatment. The linker in a drug conjugate plays a key role in the circulation time of the conjugate and release of the drug for full activity at the target site. Herein, we highlight the main linker chemistries utilized in the design of PDCs and discuss representative examples of PDCs with different linker chemistries with the related outcome in cell and animal studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
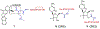

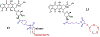



References
-
- Gotwals P; Cameron S; Cipolletta D; Cremasco V; Crystal A; Hewes B; Mueller B; Quaratino S; Sabatos-Peyton C; Petruzzelli L; Engelman JA; Dranoff G, Prospects for combining targeted and conventional cancer therapy with immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2017, 17 (5), 286–301. - PubMed
-
- Chau CH; Steeg PS; Figg WD, Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer. Lancet 2019, 394 (10200), 793–804. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

