Dynamics of the lens basement membrane capsule and its interaction with connective tissue-like extracapsular matrix proteins
- PMID: 33383103
- PMCID: PMC7902460
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2020.12.005
Dynamics of the lens basement membrane capsule and its interaction with connective tissue-like extracapsular matrix proteins
Abstract
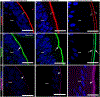
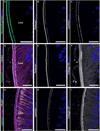
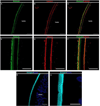
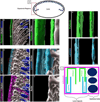
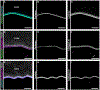
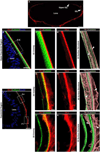
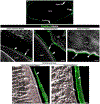
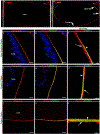
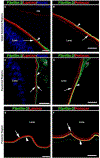
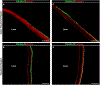
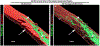
The lens, suspended in the middle of the eye by tendon-like ciliary zonule fibers and facing three different compartments of the eye, is enclosed in what has been described as the thickest basement membrane in the body. While the protein components of the capsule have been a subject of study for many years, the dynamics of capsule formation, and the region-specific relationship of its basement membrane components to one another as well as to other matrix molecules remains to be explored. Through high resolution confocal and super-resolution imaging of the lens capsule and 3D surface renderings of acquired z-stacks, our studies revealed that each of its basement membrane proteins, laminin, collagen IV, nidogen and perlecan, has unique structure, organization, and distribution specific both to the region of the lens that the capsule is located in and the position of the capsule within the eye. We provide evidence of basal membrane gradients across the depth of the capsule as well as the synthesis of distinct basement membrane lamella within the capsule. These distinctions are most prominent in the equatorial capsule zone where collagen IV and nidogen span the capsule depth, while laminin and perlecan are located in two separate lamellae located at the innermost and outermost capsule domains. We discovered that an extracapsular matrix compartment rich in the connective tissue-like matrix molecules fibronectin, tenascin-C, and fibrillin is integrated with the superficial surface of the lens capsule. Each matrix protein in this extracapsular zone also exhibits region-specific distribution with fibrils of fibrillin, the matrix protein that forms the backbone of the ciliary zonules, inserting within the laminin/perlecan lamella at the surface of the equatorial lens capsule.
Keywords: Collagen IV; Fibrillin; Laminin; Lens capsule; Perlecan; Tenascin-C.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Basic components of connective tissues and extracellular matrix: elastin, fibrillin, fibulins, fibrinogen, fibronectin, laminin, tenascins and thrombospondins.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;802:31-47. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-7893-1_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24443019 Review.
-
Immunocytochemical study of extracellular matrix components during lens and neural retina regeneration in the adult newt.Exp Eye Res. 1992 Jun;54(6):861-70. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(92)90149-m. Exp Eye Res. 1992. PMID: 1521579
-
An interaction between basement membrane and Alzheimer amyloid precursor proteins suggests a role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.Lab Invest. 1995 Mar;72(3):272-82. Lab Invest. 1995. PMID: 7898047
-
Inhibition of basement membrane formation by a nidogen-binding laminin gamma1-chain fragment in human skin-organotypic cocultures.J Cell Sci. 2004 May 15;117(Pt 12):2611-22. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01127. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15159456
-
Border patrol: insights into the unique role of perlecan/heparan sulfate proteoglycan 2 at cell and tissue borders.Matrix Biol. 2014 Feb;34:64-79. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Aug 31. Matrix Biol. 2014. PMID: 24001398 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Eye Lens Organoids Made Simple: Characterization of a New Three-Dimensional Organoid Model for Lens Development and Pathology.Cells. 2023 Oct 18;12(20):2478. doi: 10.3390/cells12202478. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37887322 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of Lens Progenitor Cells and Lentoid Bodies from Pluripotent Stem Cells: Novel Tools for Human Lens Development and Ocular Disease Etiology.Cells. 2022 Nov 6;11(21):3516. doi: 10.3390/cells11213516. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lens placode modulates extracellular matrix formation during early eye development.Differentiation. 2024 Jul-Aug;138:100792. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2024.100792. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Differentiation. 2024. PMID: 38935992 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoregulatory Properties of Immune Cells that Associate with the Lens Capsule Surface during Acute and Resolution Phases of Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis.Am J Pathol. 2024 Nov;194(11):2194-2211. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2024.07.021. Epub 2024 Aug 17. Am J Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39159867 Free PMC article.
-
Immune cells in lens injury repair and fibrosis.Exp Eye Res. 2021 Aug;209:108664. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108664. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Exp Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 34126081 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parmigiani C, and McAvoy J. (1984) Localisation of laminin and fibronectin during rat lens morphogenesis. Differentiation 28, 53–61 - PubMed
-
- Bystrom B, Virtanen I, Rousselle P, Gullberg D, and Pedrosa-Domellof F. (2006) Distribution of laminins in the developing human eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47, 777–785 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

