Efficacy and safety of apatinib for the treatment of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- PMID: 33383486
- PMCID: PMC7777135
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.101004
Efficacy and safety of apatinib for the treatment of AFP-producing gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: Alpha-fetoprotein-producing gastric cancer (AFPGC) poses a therapeutic challenge worldwide because of its poor prognosis. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of antiangiogenic drug apatinib in advanced AFPGC in a real-world setting.
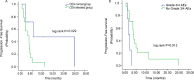
Methods: From September 2015 to December 2017, twenty-one patients identified with AFPGC from the clinical trial AHEAD-G202, an open-label, prospective, multicenter, non-interventional study of apatinib for advanced metastatic gastric cancer, were enrolled to perform this analysis. Patients received oral apatinib as monotherapy or combination therapy. A treatment cycle was defined as 28 days. The primary outcome was progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), and the secondary outcomes included safety, objective response rate (ORR), and disease control rate (DCR).
Results: Twenty patients were evaluated for the apatinib efficacy analysis. The ORR of apatinib was 10%, whereas the DCR was 70%. The median PFS was 3.5 months [95%confidence interval (CI): 2.34-4.66]. The median OS was 4.5 months (95%CI: 3.49-5.51). Median OS of AFPGC patients without carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) elevation achieved 30.8 months. CEA elevation was considered to be a potential independent predictive factor for OS (P = 0.030) and PFS (P = 0.047) by the analysis of multivariate analysis. The most common grade 3 to 4 adverse events (AEs) were hypertension (4.8%), hand-foot syndrome (4.8%), anorexia (4.8%), and vomiting and nausea (4.8%).
Conclusion: Apatinib showed promising efficacy and an acceptable safety profile in patients with advanced AFPGC. Antiangiogenic therapy may be a good strategy for the treatment of AFPGC as a rare sub-type of gastric cancer.
Trial registration: AHEAD-G202 (NCT02668380).
Keywords: AFP-producing gastric cancer; Alpha-fetoprotein; Apatinib; Target therapy.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Bergstrand C.G., Czar B. Demonstration of a new protein fraction in serum from the human fetus. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 1956;8:174–179. - PubMed
-
- Metzgeroth G., Strobel P., Baumbusch T., Reiter A., Hastka J. Hepatoid adenocarcinoma -review of the literature illustrated by a rare case originating in the peritoneal cavity. Onkologie. 2010;33:263–269. - PubMed
-
- Yamagata T., Yamagata Y., Nakanishi M., Matsunaga K., Minakata Y., Ichinose M. A case of primary lung cancer producing alpha-fetoprotein. Can. Respir. J. 2004;11:504–506. - PubMed
-
- Matsueda K., Yamamoto H., Yoshida Y., Notohara K. Hepatoid carcinoma of the pancreas producing protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist II (PIVKA-II) and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) J. Gastroenterol. 2006;41:1011–1019. - PubMed
-
- Kinjo T., Taniguchi H., Kushima R., Sekine S., Oda I., Saka M., Gotoda T., Kinjo F., Fujita J., Shimoda T. Histologic and immunohistochemical analyses of α -fetoprotein-producing cancer of the stomach. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012;36:56–65. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

