Microbial Contamination of Chicken Litter Manure and Antimicrobial Resistance Threat in an Urban Area Setting in Cameroon
- PMID: 33383622
- PMCID: PMC7824223
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10010020
Microbial Contamination of Chicken Litter Manure and Antimicrobial Resistance Threat in an Urban Area Setting in Cameroon
Abstract
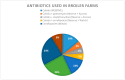
We conducted a pilot study to assess microbiological safety of chicken litter, an affordable organic and main fertilizer used in Cameroon and worldwide. A convenience sampling of 26 farms was done and a questionnaire was administered. Samples of litter were aseptically collected. E. coli and Salmonella spp. were isolated using CLSI standards. Antibiotic susceptibility testing was performed using the disc diffusion method and a micro broth dilution method for colistin. In broiler farms, 90% of participating farmers gave antibiotic prophylaxis. The prevalence of E. coli and Salmonella spp. was 59.1% and 15.5%, respectively. All E. coli isolates were multidrug resistant as well as 36.4% for Salmonella spp. No resistance was found against cefepime and imipenem. All Salmonella spp. tested were found sensitive to colistin while 26.7% of E. coli spp. were colistin resistant. Contamination of chicken litter may be an underestimated source of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) transmission towards animals, humans and the environment with multidrug resistant E. coli and Salmonella spp. This shows the need and opportunity for a One Health approach in AMR surveillance and control in Cameroon. Continued surveillance in chicken litter would enable monitoring of AMR risks and trends.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; chicken litter manure; veterinary antibiotic use.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pujiastuti E.S., Tarigan J.R., Sianturi E., Ginting B.B. The effect of chicken manure and beneficial microorganisms of EM-4 on growth and yield of kale (Brassica oleraceae acephala) grown on Andisol. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018;205:012020. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/205/1/012020. - DOI
-
- Merchant L.E., Rempel H., Forge T., Kannangara T., Bittman S., Delaquis P., Topp E., Ziebell K.A., Diarra M.S. Characterization of antibiotic-resistant and potentially pathogenic Escherichia coli from soil fertilized with litter of broiler chickens fed antimicrobial-supplemented diets. Can. J. Microbiol. 2012;58:1084–1098. doi: 10.1139/w2012-082. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

