ApoE-Targeting Increases the Transfer of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles with Donepezil Cargo across a Culture Model of the Blood-Brain Barrier
- PMID: 33383743
- PMCID: PMC7824445
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13010038
ApoE-Targeting Increases the Transfer of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles with Donepezil Cargo across a Culture Model of the Blood-Brain Barrier
Abstract
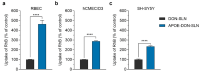
Pharmacological treatment of central nervous system (CNS) disorders is difficult, because the blood-brain barrier (BBB) restricts the penetration of many drugs into the brain. To solve this unmet therapeutic need, nanosized drug carriers are the focus of research efforts to develop drug delivery systems for the CNS. For the successful delivery of nanoparticles (NPs) to the brain, targeting ligands on their surface is necessary. Our research aim was to design a nanoscale drug delivery system for a more efficient transfer of donepezil, an anticholinergic drug in the therapy of Alzheimer's disease across the BBB. Rhodamine B-labeled solid lipid nanoparticles with donepezil cargo were prepared and targeted with apolipoprotein E (ApoE), a ligand of BBB receptors. Nanoparticles were characterized by measurement of size, polydispersity index, zeta potential, thermal analysis, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, in vitro release, and stability. Cytotoxicity of nanoparticles were investigated by metabolic assay and impedance-based cell analysis. ApoE-targeting increased the uptake of lipid nanoparticles in cultured brain endothelial cells and neurons. Furthermore, the permeability of ApoE-targeted nanoparticles across a co-culture model of the BBB was also elevated. Our data indicate that ApoE, which binds BBB receptors, can potentially be exploited for successful CNS targeting of solid lipid nanoparticles.
Keywords: ApoE; blood–brain barrier; donepezil; drug delivery to brain; solid lipid nanoparticle; targeted drug delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Niosomes decorated with dual ligands targeting brain endothelial transporters increase cargo penetration across the blood-brain barrier.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018 Oct 15;123:228-240. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2018.07.042. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 30031862
-
A Triple Combination of Targeting Ligands Increases the Penetration of Nanoparticles across a Blood-Brain Barrier Culture Model.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 30;14(1):86. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010086. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 35056983 Free PMC article.
-
Alanine and glutathione targeting of dopamine- or ibuprofen-coupled polypeptide nanocarriers increases both crossing and protective effects on a blood-brain barrier model.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2025 Feb 19;22(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12987-025-00623-2. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2025. PMID: 39972353 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid nanoparticles strategies to modify pharmacokinetics of central nervous system targeting drugs: Crossing or circumventing the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to manage neurological disorders.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Oct;189:114485. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114485. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35970274 Review.
-
Cellular and Molecular Targeted Drug Delivery in Central Nervous System Cancers: Advances in Targeting Strategies.Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(30):2762-2776. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666200826122402. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32851962 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased Cellular Uptake of ApoE3- or c(RGD)-Modified Liposomes for Glioblastoma Therapy Depending on the Target Cells.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Aug 23;16(9):1112. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16091112. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39339149 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-targeted delivery of Valsartan using solid lipid nanoparticles labeled with Rhodamine B; a promising technique for mitigating the negative effects of stroke.Drug Deliv. 2023 Dec;30(1):2179127. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2023.2179127. Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 36794404 Free PMC article.
-
Parenteral Lipid-Based Nanoparticles for CNS Disorders: Integrating Various Facets of Preclinical Evaluation towards More Effective Clinical Translation.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 29;15(2):443. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020443. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intranasal Polymeric and Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for CNS Drug Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 23;15(3):746. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030746. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regenerative Medicine in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease: A Narrative Review.Iran J Public Health. 2025 Jul;54(7):1399-1410. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v54i7.19146. Iran J Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40777911 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
- TUBITAK- 2214 International Doctoral Research Fellowship Programme/Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey
- 18L0237011/Ankara University
- NNE-29617/National Research, Development and Innovation Office of Hungary
- GINOP-2.2.1-15-2016-00007/National Research, Development and Innovation Office of Hungary
- GINOP-2.3.2-15-2016-00060/National Research, Development and Innovation Office of Hungary
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

