Insight into the bZIP Gene Family in Solanum tuberosum: Genome and Transcriptome Analysis to Understand the Roles of Gene Diversification in Spatiotemporal Gene Expression and Function
- PMID: 33383823
- PMCID: PMC7796262
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22010253
Insight into the bZIP Gene Family in Solanum tuberosum: Genome and Transcriptome Analysis to Understand the Roles of Gene Diversification in Spatiotemporal Gene Expression and Function
Abstract
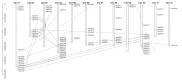
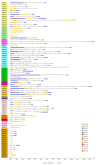
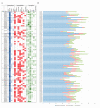
The basic region-leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors (TFs) form homodimers and heterodimers via the coil-coil region. The bZIP dimerization network influences gene expression across plant development and in response to a range of environmental stresses. The recent release of the most comprehensive potato reference genome was used to identify 80 StbZIP genes and to characterize their gene structure, phylogenetic relationships, and gene expression profiles. The StbZIP genes have undergone 22 segmental and one tandem duplication events. Ka/Ks analysis suggested that most duplications experienced purifying selection. Amino acid sequence alignments and phylogenetic comparisons made with the Arabidopsis bZIP family were used to assign the StbZIP genes to functional groups based on the Arabidopsis orthologs. The patterns of introns and exons were conserved within the assigned functional groups which are supportive of the phylogeny and evidence of a common progenitor. Inspection of the leucine repeat heptads within the bZIP domains identified a pattern of attractive pairs favoring homodimerization, and repulsive pairs favoring heterodimerization. These patterns of attractive and repulsive heptads were similar within each functional group for Arabidopsis and S. tuberosum orthologs. High-throughput RNA-seq data indicated the most highly expressed and repressed genes that might play significant roles in tissue growth and development, abiotic stress response, and response to pathogens including Potato virus X. These data provide useful information for further functional analysis of the StbZIP gene family and their potential applications in crop improvement.
Keywords: RNA sequence analysis; Solanum tuberosum; bZIP transcription factor family; drought stress response; gene regulatory networks; genomic survey; heat stress response; potato genome; potato transcriptome; stress physiology and genetics; tuber genome; virus stress response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Systematic identification and functional analysis of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) bZIP transcription factors and overexpression of potato bZIP transcription factor StbZIP-65 enhances salt tolerance.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Oct 15;161:155-167. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.032. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32512099
-
Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of basic leucine zipper transcription factors following abiotic stresses in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.).PLoS One. 2021 Mar 12;16(3):e0247864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247864. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33711039 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis and expression profile of the bZIP transcription factor gene family in grapevine (Vitis vinifera).BMC Genomics. 2014 Apr 13;15:281. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-281. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24725365 Free PMC article.
-
Abscisic-acid-dependent basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors in plant abiotic stress.Protoplasma. 2017 Jan;254(1):3-16. doi: 10.1007/s00709-015-0920-4. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Protoplasma. 2017. PMID: 26669319 Review.
-
Role of bZIP Transcription Factors in Plant Salt Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 26;24(9):7893. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097893. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175598 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The plant endoplasmic reticulum UPRome: A repository and pathway browser for genes involved in signaling networks linked to the endoplasmic reticulum.Plant Direct. 2022 Jul 20;6(7):e431. doi: 10.1002/pld3.431. eCollection 2022 Jul. Plant Direct. 2022. PMID: 35875835 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Functional Analysis of bZIP Genes in Cotton Response to Drought Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 28;23(23):14894. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314894. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499218 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Characterization and Expression Analysis of bZIP Gene Family Under Abiotic Stress in Glycyrrhiza uralensis.Front Genet. 2021 Oct 5;12:754237. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.754237. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34675967 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Regulatory Networks Associate with Early Stages of Potato Virus X Infection of Solanum tuberosum.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 11;22(6):2837. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062837. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33799566 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying and Characterizing Candidate Genes Contributing to a Grain Yield QTL in Wheat.Plants (Basel). 2023 Dec 20;13(1):26. doi: 10.3390/plants13010026. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38202333 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

