Phloroglucinol Derivatives from Dryopteris crassirhizoma as Potent Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors
- PMID: 33383880
- PMCID: PMC7796287
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26010122
Phloroglucinol Derivatives from Dryopteris crassirhizoma as Potent Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors
Abstract
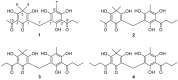
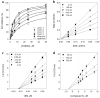
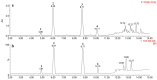
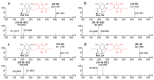
Dryopteris crassirhizoma rhizomes are used as a traditional medicine in Asia. The EtOAc extract of these roots has shown potent xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitory activity. However, the main phloroglucinols in D. crassirhizoma rhizomes have not been analyzed. Thus, we investigated the major constituents responsible for this effect. Bioassay-guided purification isolated four compounds: flavaspidic acid AP (1), flavaspidic acid AB (2), flavaspidic acid PB (3), and flavaspidic acid BB (4). Among these, 1 showed the most potent inhibitory activity with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value of 6.3 µM, similar to that of allopurinol (IC50 = 5.7 µM) and better than that of oxypurinol (IC50 = 43.1 µM), which are XO inhibitors. A comparative activity screen indicated that the acetyl group at C3 and C3' is crucial for XO inhibition. For example, 1 showed nearly 4-fold higher efficacy than 4 (IC50 = 20.9 µM). Representative inhibitors (1-4) in the rhizomes of D. crassirhizoma showed reversible and noncompetitive inhibition toward XO. Furthermore, the potent inhibitors were shown to be present in high quantities in the rhizomes by a UPLC-QTOF-MS analysis. Therefore, the rhizomes of D. crassirhizoma could be used to develop nutraceuticals and medicines for the treatment of gout.
Keywords: Dryopteris crassirhizoma; flavaspidic acid; gout; phloroglucinols; traditional medicine; xanthine oxidase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibacterial activity of two phloroglucinols, flavaspidic acids AB and PB, from Dryopteris crassirhizoma.Arch Pharm Res. 2009 May;32(5):655-9. doi: 10.1007/s12272-009-1502-9. Epub 2009 May 27. Arch Pharm Res. 2009. PMID: 19471878 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant activity of two phloroglucinol derivatives from Dryopteris crassirhizoma.Biol Pharm Bull. 2003 Sep;26(9):1354-6. doi: 10.1248/bpb.26.1354. Biol Pharm Bull. 2003. PMID: 12951487
-
Anti-Influenza Virus (H5N1) Activity Screening on the Phloroglucinols from Rhizomes of Dryopteris crassirhizoma.Molecules. 2017 Mar 8;22(3):431. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030431. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28282885 Free PMC article.
-
An updated patent review: xanthine oxidase inhibitors for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout (2011-2015).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Mar;27(3):311-345. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2017.1261111. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017. PMID: 27841045 Review.
-
Xanthine oxidase inhibitors: patent landscape and clinical development (2015-2020).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2020 Oct;30(10):769-780. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2020.1811233. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2020. PMID: 32797760 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Hypouricemic Effect of Bioactive Compounds: Molecular Evidence and Potential Application in the Management of Gout.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Oct 25;44(11):5173-5190. doi: 10.3390/cimb44110352. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36354664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory Activity of Bioactive Phloroglucinols from the Rhizomes of Dryopteris crassirhizoma on Escherichia coli β-Glucuronidase: Kinetic Analysis and Molecular Docking Studies.Metabolites. 2022 Oct 2;12(10):938. doi: 10.3390/metabo12100938. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36295840 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Chemical Diversity and Potential Health-Promoting Effects of Ferns.Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 23;13(18):2668. doi: 10.3390/plants13182668. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39339643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Dryopteris crassirhizoma Using Artificial Neural Network and Response Surface Methodology.Metabolites. 2023 Apr 13;13(4):557. doi: 10.3390/metabo13040557. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37110215 Free PMC article.
-
Potential herb‒drug interactions between anti-COVID-19 drugs and traditional Chinese medicine.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Jun 5;13(9):3598-637. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.06.001. Online ahead of print. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37360014 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fukunari A., Okamoto K., Nishino T.B., Eger T., Pai E.F., Kamezawa M., Yamada I., Kato N. Y-700 [1-[3-Cyano-4-(2,2-dimethylpropoxy)phenyl]-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid]: A potent xanthine oxidoreductase inhibitor with hepatic excretion. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004;311:519–528. doi: 10.1124/jpet.104.070433. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

