Microfluidic Device with an Integrated Freeze-Dried Cell-Free Protein Synthesis System for Small-Volume Biosensing
- PMID: 33383890
- PMCID: PMC7824204
- DOI: 10.3390/mi12010027
Microfluidic Device with an Integrated Freeze-Dried Cell-Free Protein Synthesis System for Small-Volume Biosensing
Abstract
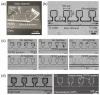
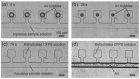
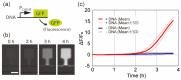
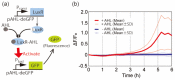
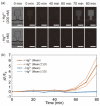
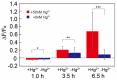
Microfluidic devices enable the precise operation of liquid samples in small volumes. This motivates why microfluidic devices have been applied to point-of-care (PoC) liquid biopsy. Among PoC liquid biopsy studies, some report diagnostic reagents being freeze-dried in such microfluidic devices. This type of PoC microfluidic device has distinct advantages, such as simplicity of the procedures, compared with other PoC devices using liquid-type diagnostic reagents. Despite the attractive characteristic, only diagnostic reagents based on the cloned enzyme donor immunoassay (CEDIA) have been freeze-dried in the microfluidic device. However, development of the PoC device based on the CEDIA method is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Here, we employed a molecule-responsive protein synthesis system as the diagnostic reagent to be freeze-dried in the microfluidic device. Such molecule-responsive protein synthesis has been well investigated in the field of molecular biology. Therefore, using the accumulated information, PoC devices can be efficiently developed. Thus, we developed a microfluidic device with an integrated freeze-dried molecule-responsive protein synthesis system. Using the developed device, we detected two types of bio-functional molecules (i.e., bacterial quorum sensing molecules and mercury ions) by injecting 1 µL of sample solution containing these molecules. We showed that the developed device is applicable for small-volume biosensing.
Keywords: cell-free protein synthesis (CFPS); freeze-dry; microfluidic device; point-of-care (PoC).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lab-on-a-Disc for Point-of-Care Infection Diagnostics.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Oct 5;54(19):3643-3655. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00367. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34516092
-
Immuno-biosensor on a chip: a self-powered microfluidic-based electrochemical biosensing platform for point-of-care quantification of proteins.Lab Chip. 2021 Dec 21;22(1):108-120. doi: 10.1039/d1lc00879j. Lab Chip. 2021. PMID: 34860233
-
Dried reagents for multiplex genotyping by tag-array minisequencing to be used in microfluidic devices.Analyst. 2010 Sep;135(9):2377-85. doi: 10.1039/c0an00321b. Epub 2010 Jul 29. Analyst. 2010. PMID: 20668755
-
A critical insight into the development pipeline of microfluidic immunoassay devices for the sensitive quantitation of protein biomarkers at the point of care.Analyst. 2017 Mar 13;142(6):858-882. doi: 10.1039/c6an02445a. Analyst. 2017. PMID: 28217778 Review.
-
Cancer Liquid Biopsy Using Integrated Microfluidic Exosome Analysis Platforms.Biotechnol J. 2020 May;15(5):e1900225. doi: 10.1002/biot.201900225. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 32032977 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-Free PURE System: Evolution and Achievements.Biodes Res. 2022 Aug 30;2022:9847014. doi: 10.34133/2022/9847014. eCollection 2022. Biodes Res. 2022. PMID: 37850137 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kulinsky L., Noroozi Z., Madou M. Present technology and future trends in point-of-care microfluidic diagnostics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013;949:3–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

