Chemical Composition of a Novel Distillate from Fermented Mixture of Nine Anti-Inflammatory Herbs and Its UVB-Protective Efficacy in Mouse Dorsal Skin via Attenuating Collagen Disruption and Inflammation
- PMID: 33383913
- PMCID: PMC7795019
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26010124
Chemical Composition of a Novel Distillate from Fermented Mixture of Nine Anti-Inflammatory Herbs and Its UVB-Protective Efficacy in Mouse Dorsal Skin via Attenuating Collagen Disruption and Inflammation
Abstract
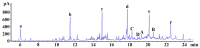
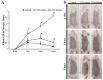
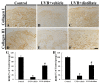
Since ancient times, various herbs have been used in Asia, including Korea, China, and Japan, for wound healing and antiaging of the skin. In this study, we manufactured and chemically analyzed a novel distillate obtained from a fermented mixture of nine anti-inflammatory herbs (Angelica gigas, Lonicera japonica, Dictamnus dasycarpus Turcz., D. opposita Thunb., Ulmus davidiana var. japonica, Hordeum vulgare var. hexastichon Aschers., Xanthium strumarium L., Cnidium officinale, and Houttuynia cordata Thunb.). The fermentation of natural plants possesses beneficial effects in living systems. These activities are attributed to the chemical conversion of the parent plants to functional constituents which show more potent biological activities. In our current study, the distillate has been manufactured after fermenting the nine oriental medical plants with Lactobacillus fermentum, followed by distilling. We analyzed the chemical ingredients involved in the distillate and evaluated the effects of topical application of the distillate on ultraviolet B (UVB)-induced skin damage in Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice. Topical application of the distillate significantly ameliorated the macroscopic and microscopic morphology of the dorsal skin against photodamage induced by UVB radiation. Additionally, our current results showed that topical application of the distillate alleviated collagen disruption and reduced levels of proinflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 β expressions) in the dorsal skin against UVB radiation. Taken together, our current findings suggest that the distillate has a potential to be used as a material to develop a photoprotective adjuvant.
Keywords: UVB; distillation; fermentation; natural herb complex; skin protection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oenanthe Javanica Extract Protects Mouse Skin from UVB Radiation via Attenuating Collagen Disruption and Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 21;20(6):1435. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061435. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30901885 Free PMC article.
-
Photoprotection of Buddleja cordata extract against UVB-induced skin damage in SKH-1 hairless mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Aug 3;14:281. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-281. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25086781 Free PMC article.
-
Topical Application of Aronia melanocarpa Extract Rich in Chlorogenic Acid and Rutin Reduces UVB-Induced Skin Damage via Attenuating Collagen Disruption in Mice.Molecules. 2020 Oct 7;25(19):4577. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194577. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33036412 Free PMC article.
-
An organotypic model of skin to study photodamage and photoprotection in vitro.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008 May;58(5 Suppl 2):S155-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.08.050. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18410802 Review.
-
Natural components in sunscreens: Topical formulations with sun protection factor (SPF).Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Feb;134:111161. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111161. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33360043 Review.
Cited by
-
Accelerated Oral Healing by Angelica gigas Nakai from Hot Melt Extrusion Technology: An In Vitro Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Nov 23;59(12):2066. doi: 10.3390/medicina59122066. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38138169 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Verification of a Precolumn Derivatization LC-MS/MS Method for the Pharmacokinetic Study of Houttuynine of Houttuynia Essential Oil.Molecules. 2021 Apr 16;26(8):2327. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082327. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33923761 Free PMC article.
-
Rg3 and Rh2 ginsenosides suppress embryoid body formation by inhibiting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Arch Pharm Res. 2022 Jul;45(7):494-505. doi: 10.1007/s12272-022-01395-1. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Arch Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 35759089
-
A critical overview of challenging roles of medicinal plants in improvement of wound healing technology.Daru. 2024 Jun;32(1):379-419. doi: 10.1007/s40199-023-00502-x. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Daru. 2024. PMID: 38225520 Free PMC article.
-
Soil volatilomics uncovers tight linkage between soybean presence and soil omics profiles in agricultural fields.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 4;14(1):20541. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70873-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39232061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pillai S., Oresajo C., Hayward J. Ultraviolet radiation and skin aging: Roles of reactive oxygen species, inflammation and protease activation, and strategies for prevention of inflammation-induced matrix degradation—A review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2005;27:17–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-2494.2004.00241.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahn J.H., Kim D.W., Park C.W., Kim B., Sim H., Kim H.S., Lee T.K., Lee J.C., Yang G.E., Her Y., et al. Laminarin Attenuates Ultraviolet-Induced Skin Damage by Reducing Superoxide Anion Levels and Increasing Endogenous Antioxidants in the Dorsal Skin of Mice. Mar. Drugs. 2020;18:345. doi: 10.3390/md18070345. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kligman L., Kligman A. The nature of photoaging: Its prevention and repair. Photodermatology. 1986;3:215–227. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

