Epiretinal Membrane Surgery: Structural Retinal Changes Correlate with the Improvement of Visual Function
- PMID: 33383922
- PMCID: PMC7795238
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10010090
Epiretinal Membrane Surgery: Structural Retinal Changes Correlate with the Improvement of Visual Function
Abstract
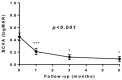
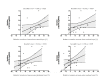
Several parameters have been studied for identifying the visual outcomes after pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) for epiretinal membrane (ERM) peeling. This retrospective study aimed to analyze structural retinal changes with spectral domain-optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) and their correlations with visual acuity improvement in patients with ERM undergoing PPV. Twenty-one pseudophakic eyes were enrolled in the study. Ophthalmic evaluations included best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and retinal layer thickness measurements with SD-OCT. The segmentation of the retina was divided into four parts: the inner retinal layer (IRL), composed of an internal limiting membrane, retinal nerve fiber layer, ganglion cell layer, and inner plexiform layer; inner nuclear layer (INL); outer plexiform layer (OPL); and outer nuclear layer (ONL). Correlations between changes in retinal layer thicknesses and BCVA were explored over a 6 month follow-up period. The postoperative thickness decrease of the INL was significantly correlated with thickness changes in all other measured retinal layers (p < 0.001). Non-parametric linear regression showed that postoperative improvement in BCVA was associated with a postoperatively decreased thickness in the IRL (p = 0.021), INL (p = 0.039), and OPL (p = 0.021). In eyes undergoing PPV, postoperative thickness decreases of the IRL, INL, and OPL were correlated with visual acuity improvements. Re-compaction of these retinal layers after relieving ERM-induced traction may be an important factor in postoperative visual function improvement.
Keywords: automated segmentation; optical coherence tomography; pars plana vitrectomy; single retinal layer; visual acuity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest relevant to this study to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Iannetti L., Accorinti M., Malagola R., Bozzoni-Pantaleoni F., Da Dalt S., Nicoletti F., Gradini R., Traficante A., Campanella M., Pivetti-Pezzi P. Role of the intravitreal growth factors in the pathogenesis of idiopathic epiretinal membrane. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011;52:5786–5789. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-7116. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Russo A., Ragusa M., Barbagallo C., Longo A., Avitabile T., Uva M.G., Bonfiglio V., Toro M.D., Caltabiano R., Mariotti C., et al. Correction: miRNAs in the vitreous humor of patients affected by idiopathic epiretinal membrane and macular hole. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0176618. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176618. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

