Sevoflurane-Induced Neuroapoptosis in Rat Dentate Gyrus Is Activated by Autophagy Through NF-κB Signaling on the Late-Stage Progenitor Granule Cells
- PMID: 33384584
- PMCID: PMC7769878
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2020.590577
Sevoflurane-Induced Neuroapoptosis in Rat Dentate Gyrus Is Activated by Autophagy Through NF-κB Signaling on the Late-Stage Progenitor Granule Cells
Abstract
Objective: The mechanisms by which exposure of the late-stage progenitor cells to the anesthesia sevoflurane alters their differentiation are not known. We seek to query whether the effects of sevoflurane on late-stage progenitor cells might be regulated by apoptosis and/or autophagy.
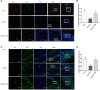
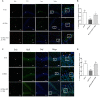
Methods: To address the short-term impact of sevoflurane exposure on granule cell differentiation, we used 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU) to identify the labeled late-stage progenitor granule cells. Male or female rats were exposed to 3% sevoflurane for 4 h when the labeled granule cells were 2 weeks old. Differentiation of the BrdU-labeled granule cells was quantified 4 and 7 days after exposure by double immunofluorescence. The expression of apoptosis and autophagy in hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG) was determined by western blot and immunofluorescence. Western blot for the expression of NF-κB was used to evaluate the mechanism. Morris water maze (MWM) test was performed to detect cognitive function in the rats on postnatal 28-33 days.
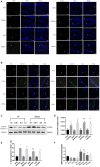
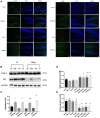
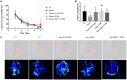
Results: Exposure to sevoflurane decreased the differentiation of the BrdU-labeled late-stage progenitor granule cells, but increased the expression of caspase-3, autophagy, and phosphorylated-P65 in the hippocampus of juvenile rats and resulted in cognitive deficiency. These damaging effects of sevoflurane could be mitigated by inhibitors of autophagy, apoptosis, and NF-κB. The increased apoptosis could be alleviated by pretreatment with the autophagy inhibitor 3-MA, and the increased autophagy and apoptosis could be reduced by pretreatment with NF-κB inhibitor BAY 11-7085.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that a single, prolonged sevoflurane exposure could impair the differentiation of late-stage progenitor granule cells in hippocampal DG and cause cognitive deficits possibly via apoptosis activated by autophagy through NF-κB signaling. Our results do not preclude the possibility that the affected differentiation and functional deficits may be caused by depletion of the progenitors pool.
Keywords: NF-κB; apoptosis; autophagy; dentate gyrus; differentiation; sevoflurane.
Copyright © 2020 Tong, Ma, Su, Wang, Xu, Zhang, Wu, Liu and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

