The Functional Availability of Arterial Kv7 Channels Is Suppressed Considerably by Large-Conductance Calcium-Activated Potassium Channels in 2- to 3-Month Old but Not in 10- to 15-Day Old Rats
- PMID: 33384611
- PMCID: PMC7770149
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.597395
The Functional Availability of Arterial Kv7 Channels Is Suppressed Considerably by Large-Conductance Calcium-Activated Potassium Channels in 2- to 3-Month Old but Not in 10- to 15-Day Old Rats
Abstract
Background: Voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels, especially Kv7 channels, are major potassium channels identified in vascular smooth muscle cells with a great, albeit differential functional impact in various vessels. Vascular smooth muscle Kv7 channels always coexist with other K channels, in particular with BK channels. BK channels differ in the extent to which they influence vascular contractility. Whether this difference also causes the variability in the functional impact of Kv7 channels is unknown. Therefore, this study addressed the hypothesis that the functional impact of Kv7 channels depends on BK channels.
Experimental approach: Experiments were performed on young and adult rat gracilis and saphenous arteries using real-time PCR as well as pressure and wire myography.
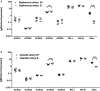
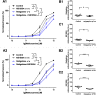
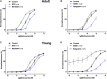
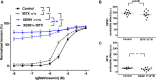
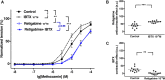
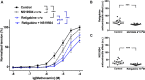
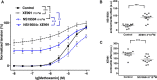
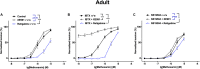
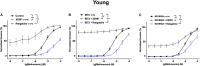
Key results: Several subfamily members of Kv7 (KCNQ) and BK channels were expressed in saphenous and gracilis arteries: the highest expression was observed for BKα, BKβ1 and KCNQ4. Arterial contractility was assessed with methoxamine-induced contractions and pressure-induced myogenic responses. In vessels of adult rats, inhibition of Kv7 channels or BK channels by XE991 or IBTX, respectively enhanced arterial contractility to a similar degree, whereas activation of Kv7 channels or BK channels by retigabine or NS19504, respectively reduced arterial contractility to a similar degree. Further, IBTX increased both the contractile effect of XE991 and the anticontractile effect of retigabine, whereas NS19504 reduced the effect of retigabine and impaired the effect of XE991. In vessels of young rats, inhibition of Kv7 channels by XE991 enhanced arterial contractility much stronger than inhibition of BK channels by IBTX, whereas activation of Kv7 by retigabine reduced arterial contractility to a greater extent than activation of BK channels by NS19504. Further, IBTX increased the anticontractile effect of retigabine but not the contractile effect of XE991, whereas NS19504 reduced the effect of retigabine and impaired the effect of XE991.
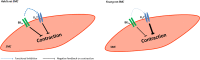
Conclusion: Kv7 and BK channels are expressed in young and adult rat arteries and function as negative feedback modulators in the regulation of contractility of these arteries. Importantly, BK channels govern the extent of functional impact of Kv7 channels. This effect depends on the relationship between the functional activities of BK and Kv7 channels.
Keywords: BK channel; Kv7 channel; arteries; ion channels; ontogenesis; vascular smooth muscle.
Copyright © 2020 Ma, Gaynullina, Schmidt, Mladenov and Schubert.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
KV7 channels are potential regulators of the exercise pressor reflex.J Neurophysiol. 2021 Jul 1;126(1):1-10. doi: 10.1152/jn.00700.2020. Epub 2021 May 26. J Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 34038189 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular Kv7 channels control intracellular Ca2+ dynamics in smooth muscle.Cell Calcium. 2020 Dec;92:102283. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2020.102283. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Cell Calcium. 2020. PMID: 32950876 Free PMC article.
-
Participation of KCNQ (Kv7) potassium channels in myogenic control of cerebral arterial diameter.J Physiol. 2010 Sep 1;588(Pt 17):3277-93. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.192823. Epub 2010 Jul 12. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20624791 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium- and voltage-gated BK channels in vascular smooth muscle.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Sep;470(9):1271-1289. doi: 10.1007/s00424-018-2151-y. Epub 2018 May 11. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 29748711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detrusor Smooth Muscle KV7 Channels: Emerging New Regulators of Urinary Bladder Function.Front Physiol. 2020 Sep 16;11:1004. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.01004. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33041840 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kv2.1 Channels Prevent Vasomotion and Safeguard Myogenic Reactivity in Rat Small Superior Cerebellar Arteries.Cells. 2023 Aug 2;12(15):1989. doi: 10.3390/cells12151989. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37566068 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of M-current activation on controller gain and obstructive sleep apnoea severity: a randomised controlled trial using flupirtine.J Physiol. 2025 May;603(10):3245-3260. doi: 10.1113/JP288337. Epub 2025 Apr 3. J Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40181609 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
TWIK-Related Acid-Sensitive Potassium Channels (TASK-1) Emerge as Contributors to Tone Regulation in Renal Arteries at Alkaline pH.Front Physiol. 2022 May 20;13:895863. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.895863. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35669582 Free PMC article.
-
Sexually dimorphic mechanisms of H2O2-mediated dilation in porcine coronary arterioles with ischemia and endurance exercise training.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2025 Apr 1;138(4):950-963. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00761.2024. Epub 2025 Mar 10. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2025. PMID: 40059640 Free PMC article.
-
Remodeling of Arterial Tone Regulation in Postnatal Development: Focus on Smooth Muscle Cell Potassium Channels.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 21;22(11):5413. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115413. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34063769 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chadha P. S., Zunke F., Zhu H.-L., Davis A. J., Jepps T. A., Olesen S. P., et al. (2012). Reduced KCNQ4-Encoded Voltage-Dependent Potassium Channel Activity Underlies Impaired β-Adrenoceptor–Mediated Relaxation of Renal Arteries in Hypertension. Hypertension 59 877–884. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.187427 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

